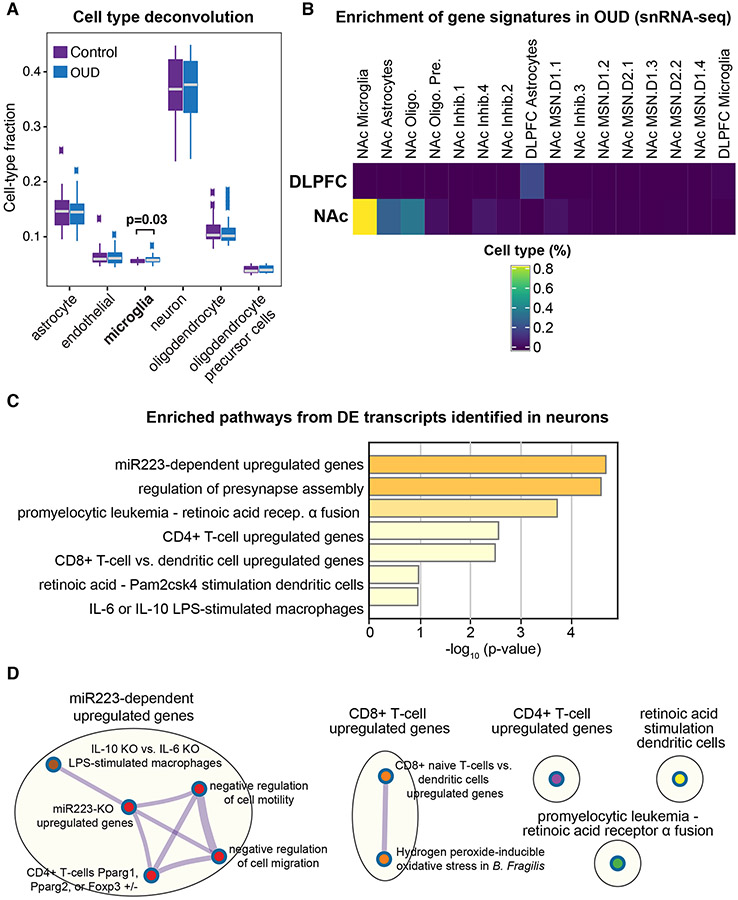
Fig. 3. Predicted microglial cell-type enrichment in both DLPFC and NAc.
A. Deconvolution analyses indicates modest difference of microglia fractions in DLPFC and NAc of OUD subjects (p<0.03; t-test controlling for brain region), consistent with enrichment of pathways in differentially expressed (DE) transcripts related to immune function. B. Using AUCell, gene signatures for DE transcripts in DLPFC and NAc in subjects with OUD was compared to signatures in various cell types from single nuclei RNA-sequencing datasets in human postmortem brains. Percent of cell type were significant in NAc microglia and DLPFC astrocytes, consistent with enrichment of transcripts related to immune function. C. Pathway enrichment analysis on the significantly altered DE transcripts in neurons identified pathways related to inflammation. D. Significantly enriched terms based on pathways included in multiple annotated sets (e.g., GO, KEGG, hallmark, etc.) using hypergeometric p-values and enrichment factors. The network is visualized with Cytoscape using Community cluster with categorical labels representing multiple clusters. Individual nodes are also labeled. Note nodes are related to presynaptic structure and function and miR233-dependent regulation of macrophage and T-cell activation. Oligo., oligodendrocytes; Oligo. Pre., oligodendrocyte precursor cells; Inhib., types of inhibitory neurons; MSN, types of medium spiny neurons, including D1 or D2, dopamine receptor subtype 1 or 2, respectively.