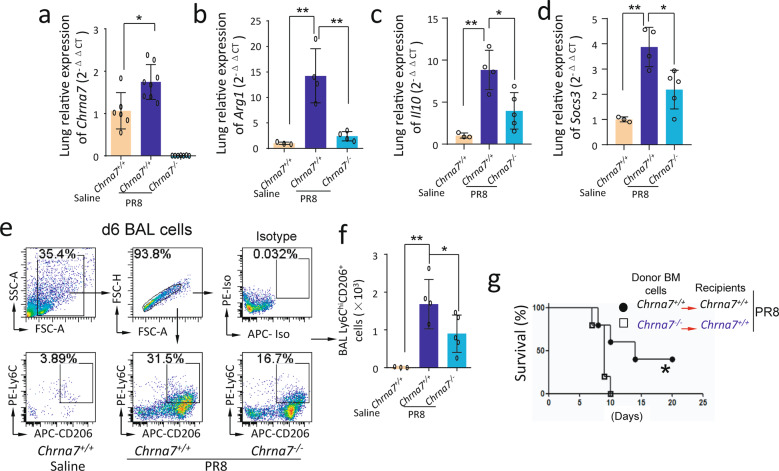
Fig. 3. Deletion of Chrna7 in bone marrow cells reduces lung anti-inflammatory responses.
a–d Saline-treated Chrna7+/+, PR8-challenged Chrna7+/+ and Chrna7−/− mice (i.n. 1.4 × 104 FFU/mouse) were sacrificed 6 dpi. The lungs were removed and homogenized for extracting RNA to detect Chrna7 (a), Arg1 (b), Il10 (c), and Socs3 (d) by qPCR. n = 3–8 in each group, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, between the indicated groups, one-way ANOVA. e–f Flow cytometry analysis of BAL Ly6ChiCD206+ cells. As stated in (a–d), BAL was performed, and cells were isolated for fluorescent antibodies staining. n = 3–5 in each group, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, between the indicated groups, one-way ANOVA. g Effect of deletion of Chrna7 in bone marrow cells on survival in influenza-induced lung infection. Chrna7+/+ recipient mice were separately reconstituted with either Chrna7+/+ or Chrna7−/− donor bone marrow. The two groups of mice were challenged with PR8 (i.n. 1.4 × 104 FFU/mouse) and followed up for 21 days. The survival was analyzed by log rank test. n = 10 in each group, *P < 0.05.