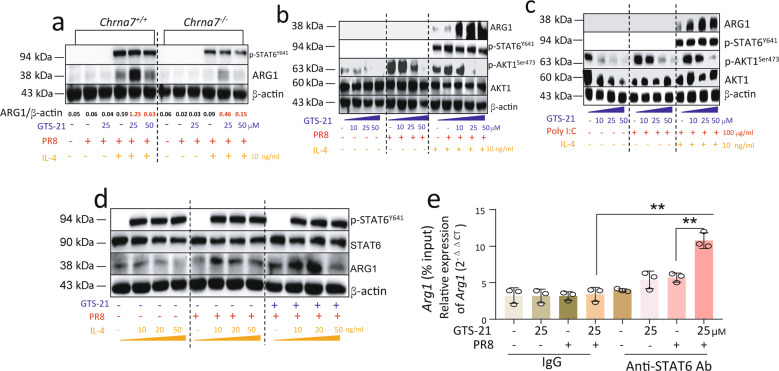
Fig. 5. Activation of α7nAChR reduces AKT1 phosphorylation and increases p-STAT6 binding with ARG1 promoter.
a Changes of ARG1, and p-STAT6 in GTS-21-PR8-IL-4 treated Chrna7+/+ or Chrna7−/− BMDM. The Chrna7+/+ or Chrna7−/− BMDM were treated according to the procedures listed in Fig. 4b. Two concentrations of GT-21 (25 and 50 μM) were used. b Using Western blot to detect dose-dependent effects of GTS-21 on ARG1, p-STAT6, and p-AKT1 in the GTS-21-PR8-IL-4 treated BMDM following procedure of Fig. 4b. GTS-21 concentration was chosen at 0, 10, 25, and 50 μM. c Using Western blot to detect dose-dependent effects of GTS-21 on ARG1, p-STAT6, and p-AKT1 in the GTS-21-Poly I:C-IL-4 treated BMDM following procedure of Fig. 4b. GTS-21 concentration was chosen at 0, 10, 25, and 50 μM. The Poly I:C concentration was 100 μg/mL. d Dose-dependent effect of IL-4 on p-STAT6 and ARG1 detected by Western blot. Experiments followed the procedures listed in Fig. 4b, but IL-4 concentration was chosen at 0, 10, 20, and 50 ng/mL. Data presented in Fig. 2a–d were repeated at least in two independent experiments. e Detecting STAT6 binding with Arg1 promoter by ChIP assay. The BMDM were treated GTS-21 (25 μM) for 30 min followed by PR8 (2 MOI) challenge for 6 h. The control groups received PBS. The data were pooled from three independent experiments, “-” condition indicated PBS treatment, **P < 0.01 in the indicated groups, unpaired t test.