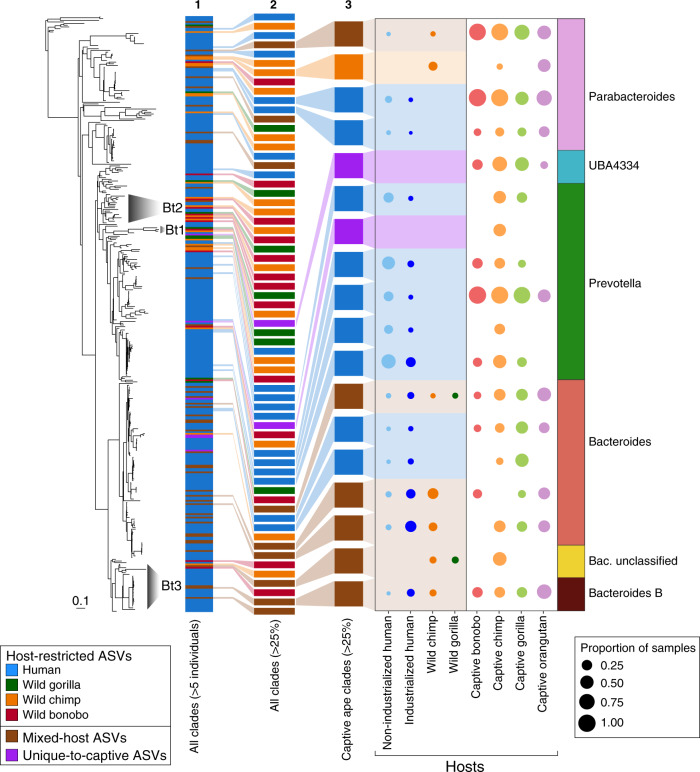
Fig. 1. Host-restricted clades of wild apes are lacking in captive apes.
Phylogeny of host-restricted clades based on gyrB-ASVs in the order Bacteroidales. In the phylogeny to the left, the three labeled and shaded clades (Bt1, Bt2, Bt3) correspond to the co-diversified lineages of Bacteroidaceae identified in Moeller et al.5. Colors in the numbered columns that follow indicate the host-species source of ASVs constituting each clade, with column 1 displaying the sources of all 356 clades present in at least five individuals, column 2 displaying only those 65 clades present in >25% of either wild or captive individuals of any host species, and column 3 displaying only those 18 clades present in >25% of captive individuals of any host species. Circles in the next two columns are shaded according to host-species source and sized to indicate the proportion of samples harboring the clade. For each of the clades prominent in captive apes (column with white background), bacterial family and genus taxonomic assignments are color-coded in the final column.