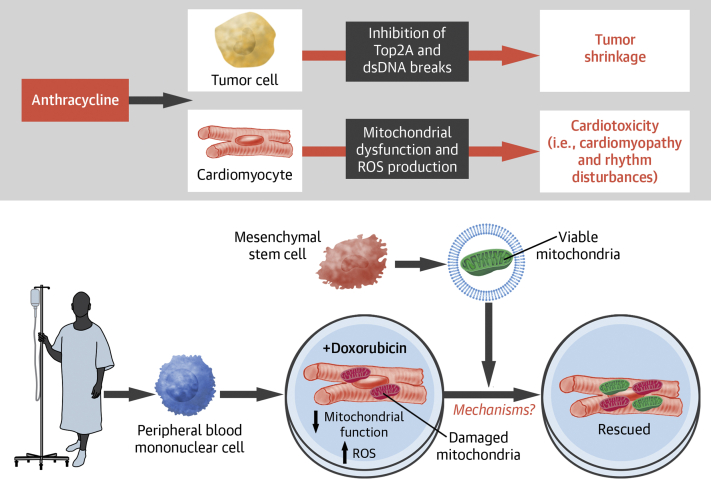
Figure 1.
AIC and an In Vitro Model of Mitochondrial Transfer as a Therapy for AIC
(Top) Anthracyclines inhibit tumor cell proliferation via inhibition of topoisomerase 2A (Top2a), which induces double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) breaks and halts cell division. In comparison, anthracyclines cause cardiotoxicity by inducing myocardial mitochondrial dysfunction and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. (Bottom) Cardiomyocytes generated from patient peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC)-derived induced pluripotent stem cells are injured by doxorubicin treatment, resulting in defective mitochondrial function and elevated ROS production. The transfer of vesicle-bound viable mitochondria derived from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) restores the mitochondrial functions of the injured cardiomyocytes. AIC = anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity; iPSC = induced pluripotent stem cell.