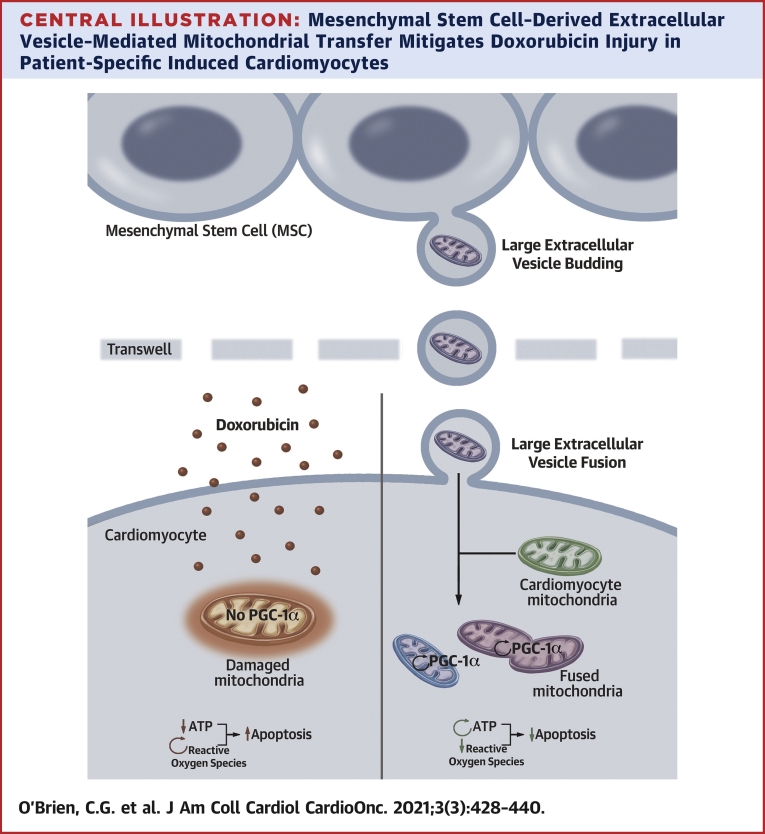
Central Illustration.
Mesenchymal Stem Cell–Derived Extracellular Vesicle–Mediated Mitochondrial Transfer Mitigates Doxorubicin Injury in Patient-Specific Induced Cardiomyocytes
Large mesenchymal stem cell extracellular vesicles (L-EVs) transit to and fuse with cardiomyocytes resulting in preserved mitochondrial function, augmentation of ATP production and Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1 (PGC-1) alpha transcription, mitigation of ROS production, and suppression of apoptosis. Up arrows indicate increased apoptosis; down arrows indicate inhibition of apoptosis; and circular arrows indicate increased production of a given molecule.