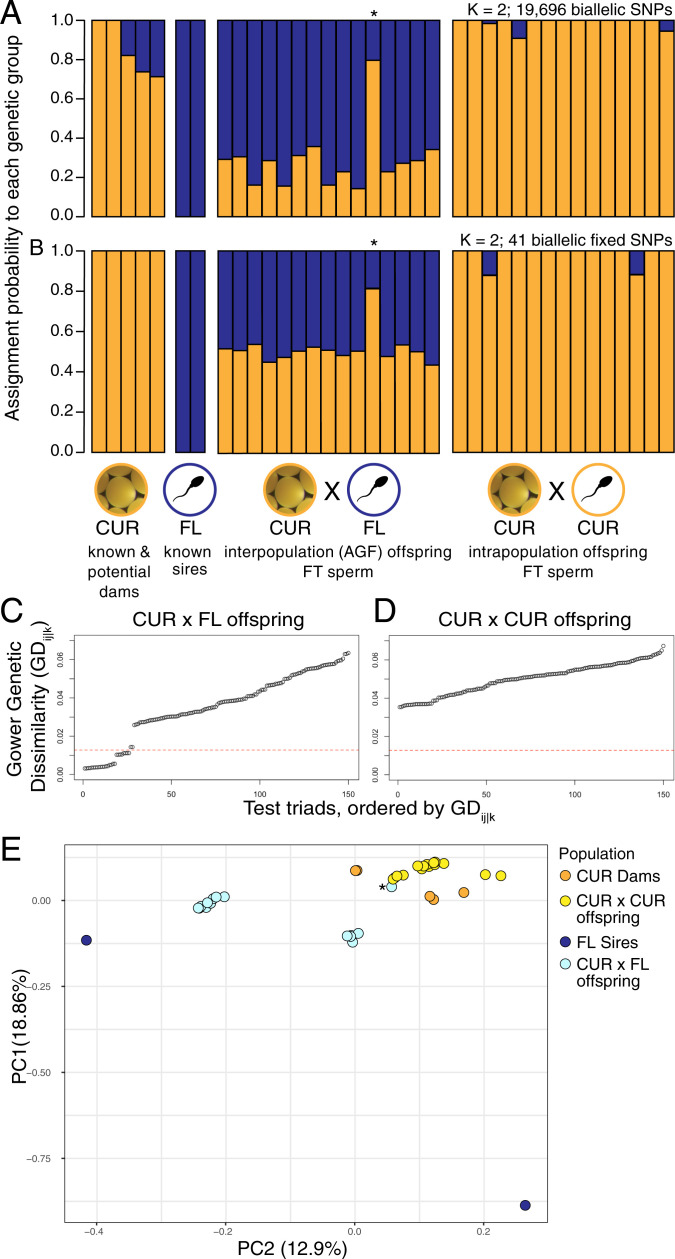
Fig. 3.
Parentage analysis of A. palmata juveniles reared from cryopreserved sperm demonstrating interpopulation parentage and successful AGF. (A and B) Genetic admixture plots for sires, dams, and offspring. The offspring genotyped for this analysis were drawn from two cohorts: CUR×FL (FT sperm, n = 15 offspring bred from n = 5 dams and n = 2 sires) and CUR×CUR (FT sperm, n = 15 offspring bred from n = 5 dams and n = 6 sires). The dataset also includes both of the known sires from Florida and five of the known and putative dams from Curaçao. The bars represent the probability of assignment (x-axis) for each individual (y-axis) to each of K = 2 genetic groups (A and B). (A) Probability of assignment using the full set of 19,696 genotyping SNPs for K = 2 populations. (B) Probability of assignment using only SNPs fixed between the Florida versus Curaçao parents (n = 41) for K = 2 populations. In (A and B), one of the juveniles from the CUR×FL cohort had a higher than expected probability of assignment to CUR (orange cluster) and is thought to be the result of self-fertilization or a labeling error (denoted with a *). (C and D) Triad assignment plots for the juveniles genotyped and analyzed Above. The data points represent the genetic dissimilarity among hypothetical triads of one sire, one dam, and one offspring. (C) Assignment plot of triads with FL sires, CUR dams, and only interpopulation (CUR×FL) offspring. A total of 13 of 15 juveniles from the interpopulation cross between FL sires (FT sperm) and CUR dams (fresh eggs) were successfully assigned to two specific parents in the sample set, shown by data points below the 0.0118 Gower genetic dissimilarity threshold. (D) Assignment plot of triads using FL sires, CUR dams, and only intrapopulation (CUR×CUR) offspring. As expected, no juveniles in the CUR×CUR cohort were assigned CUR×FL parentage (SI Appendix, Table S5 for details). (E) PCA of genetic structure among all coral dams, sires, and offspring genotyped in the analyses Above. PCA analysis was conducted using all 19,696 genotyping SNPs (R Package SNPrelate). All CUR×CUR offspring clustered with the CUR dams, while CUR×FL offspring formed a cluster in between their known FL sires and the known and putative CUR dams. As in (A and B), one CUR×FL juvenile clustered with the CUR×CUR offspring instead of with the other CUR×FL offspring, likely the result of selfing or mislabeling (denoted with a *).