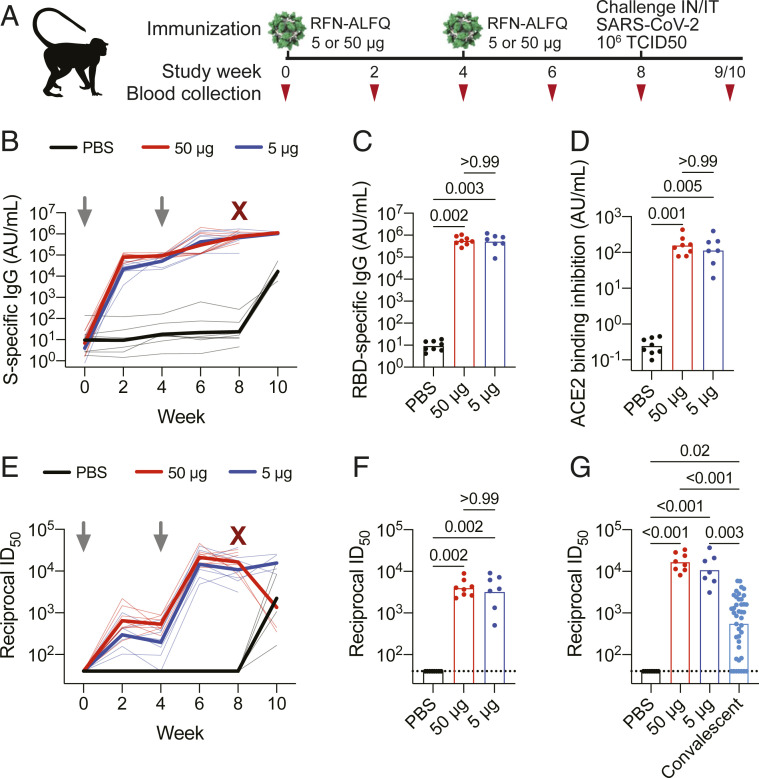
Fig. 1.
RFN vaccine−elicited binding and neutralizing antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2. Humoral immune responses were measured in vaccinated macaques. (A) Rhesus macaque vaccination, challenge, and sampling schedule. Animals were immunized with either 50 μg or 5 µg of RFN-ALFQ at weeks 0 and 4; control animals received PBS (N = 7 or 8 per group); 1 × 106 TCID50 of SARS-CoV-2 was administered 4 wk after the last vaccination. (B) Serum SARS-CoV-2 S-specific IgG responses assessed by MSD immunoassay every 2 wk following vaccination. Data are depicted as arbitrary units per milliliter of IgG binding. Thick lines indicate geometric means within each group, and thin lines represent individual animals. Serum SARS-CoV-2 RBD-specific IgG (C) and inhibition of ACE2 binding to the RBD (D) 4 wk after last vaccination were measured by MSD immunoassay. (E) Serum SARS-CoV-2 S-specific pseudovirus neutralization every 2 wk following vaccination. Virus neutralization reciprocal ID50 is shown. Thick lines indicate geometric means within each group, and thin lines represent individual animals. (F) Authentic SARS-CoV-2 WA1/2020 virus neutralization at 4 wk after last vaccination. (G) Pseudovirus neutralization activity 4 wk postboost was compared to a panel of human convalescent sera (n = 41 samples). Bars indicate the geometric mean titer. Symbols represent individual animals and overlap with one another for equal values where constrained. In B and E, gray arrows indicate the time of immunization; maroon Xs indicate time of challenge. Significance was assessed using a Kruskal−Wallis test followed by a Dunn’s posttest.