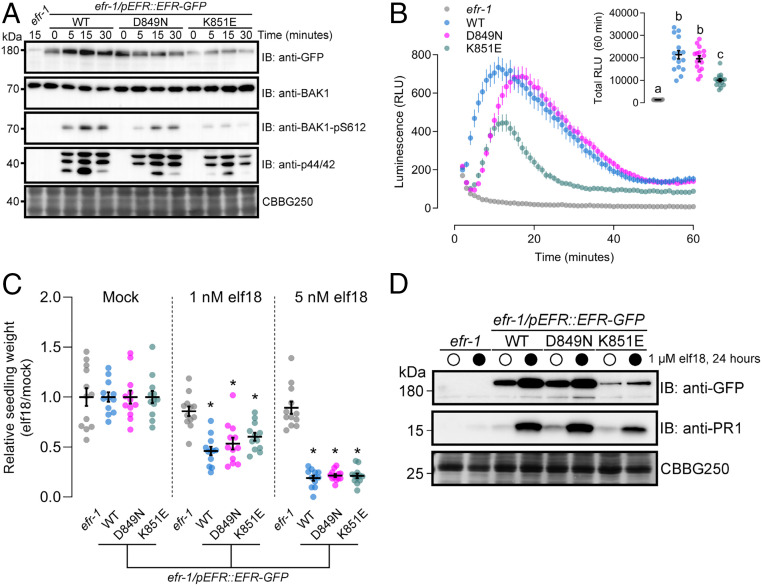
Fig. 2.
Catalytically inactive EFR variants are competent for elf18-induced PTI signaling. (A) Immunoblot analysis of elf18-induced phosphorylation of BAK1 (anti-BAK1-pS612) and MAPKs (anti-p44/42) in 12-d-old seedlings treated with 1 µM elf18 for the indicated time. Anti-GFP shows protein accumulation of EFR and the site-directed mutants. Anti-BAK1 shows similar abundance of the coreceptor across all samples. Coomassie stain is shown as loading control (CBBG250). Blotting experiments were performed three times with similar results. (B) Time course of the oxidative burst in leaf discs from transgenic Arabidopsis expressing EFR-GFP (WT) or kinase-dead variants (D849N or K851E) in the efr-1 knockout background induced by treatment with 100 nM elf18. Points are mean with SEM. Inset shows mean with SEM of total luminescence over 60 min with individual data points. Means with like letter designations are not statistically different (Kruskal–Wallis ANOVA, n = 16 leaf discs, P < 0.000001, Dunn’s multiple comparisons test). The experiment was repeated three times with similar results. (C) Relative weight of seedlings grown in liquid media for 10 d with (1 or 5 nM) or without (Mock) the addition of elf18 peptide. Mean with SEM and individual values are shown. Asterisk indicates statistical difference from efr-1 within a given treatment (two-way ANOVA, n = 12 seedlings, P < 0.0001, Dunnett’s multiple comparison test). The experiment was repeated three times with similar results. (D) Accumulation of PR1 protein assessed by immunoblotting with anti-PR1 antibodies 24 h after infiltration of leaves from 3-wk-old plants with mock (open circles) or 1 µM elf18 (closed circles). Coomassie stain is shown as loading control (CBBG250). PR1 accumulation was assessed in three independent experiments with similar results each time.