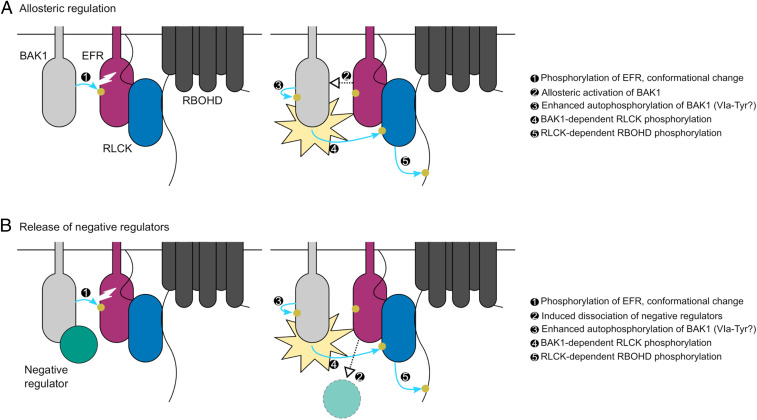
Fig. 7.
Potential mechanisms for phosphorylation-mediated activation of plant non-RD LRR-RK complexes. Ligand-triggered dimerization promotes phosphorylation of the EFR (purple) activation loop by BAK1 (light gray), inducing a conformational change of the EFR cytoplasmic domain. This conformational rearrangement feeds forward on BAK1 to enhance its catalytic activity either: (A) by direct allosteric activation of BAK1 or (B) by triggering the release of negative regulators (teal) of BAK1 activation. Either scenario permits full phosphorylation of the complex including on the VIa-Tyr residues. After full activation, BAK1 can phosphorylate the executor RLCKs (blue) to initiate downstream signaling, for example the RBOHD (dark gray)-dependent apoplastic oxidative burst. Yellow circles and blue arrows represent simplified requirements for activation of RBOHD-dependent ROS production by phosphorylation.