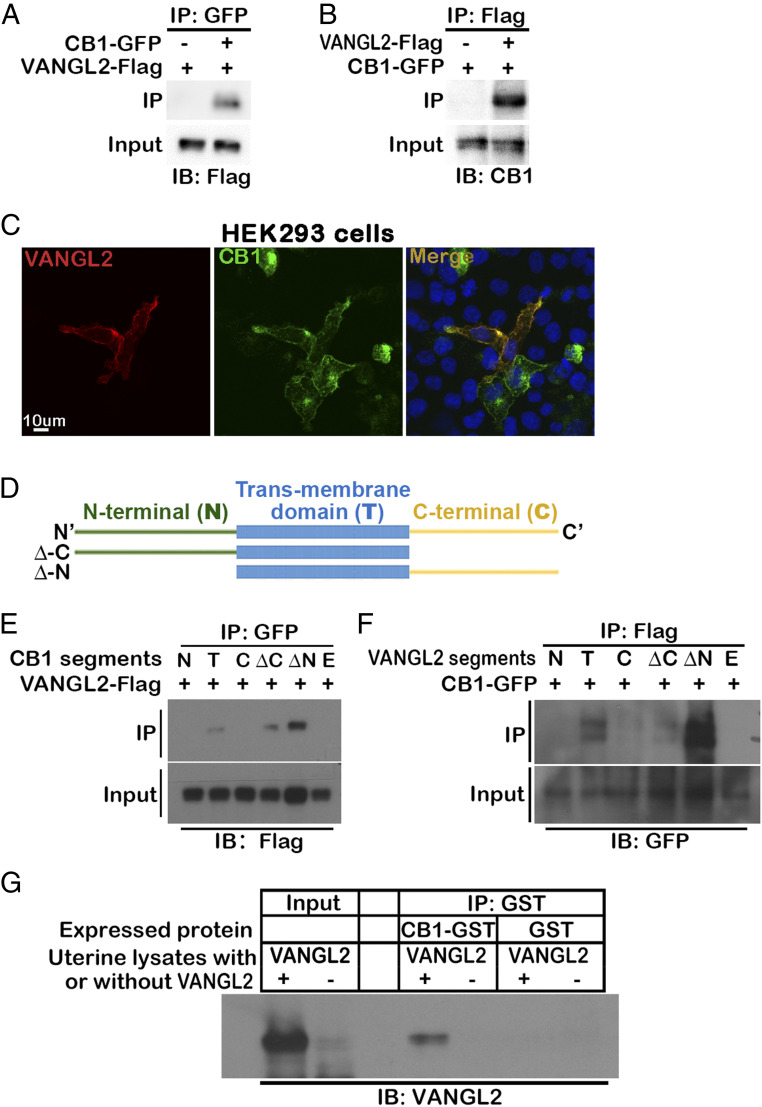
Fig. 1.
VANGL2 physically associated with CB1 promotes TS migration. (A and B) CB1 is physically associated with VANGL2. Co-IP experiments are performed in HEK293T cells cotransfected with CB1-GFP and VANGL2-Flag vectors. VANGL2-Flag or CB1-GFP proteins are detected in the lysates immunoprecipitated by either GFP or Flag antibody, respectively. (C) Colocalization of CB1 and VANGL2 in HEK293T cells. HEK293T cells are cotransfected with CB1-GFP and VANGL2-Flag vectors, and signals are revealed by GFP and immunostaining of the Flag tag. (Scale bar, 10 μm.) (D) Illustration of different segments cloned for CB1 and VANGL2. (E) VANGL2 pulls down CB1 segments with transmembrane domains. Different segments of CB1 with GFP tags were cotransfected with VANGL2-Flag into HEK293T cells. (F) CB1 pulls down VANGL2 segments with transmembrane domains. Different segments of VANGL2 with tags were cotransfected with CB1-GFP into HEK293T cells. (G) The interaction of CB1 and VANGL2 is confirmed using CB1 purified from bacteria culture and VANGL2 in uterine lysates. CB1-GST purified from BL21 bacteria culture lysates is incubated with Vangl2f/fPgr+/+ (VANGL2+) uterine protein lysates from day 4 of pregnancy, and a GST antibody immunoprecipitates VANGL2. BL21 bacteria transformed with GST-only plasmids are used for negative control of CB1. Vangl2f/fPgrcre/+ (VANGL2-) uterine protein lysates serve as negative controls of VANGL2. IB, immunoblotting; N, N-terminal; T, transmembrane; C, C-terminal; ΔC, full length without C-terminal; ΔN, full length without N-terminal; F, full length; E, empty vector.