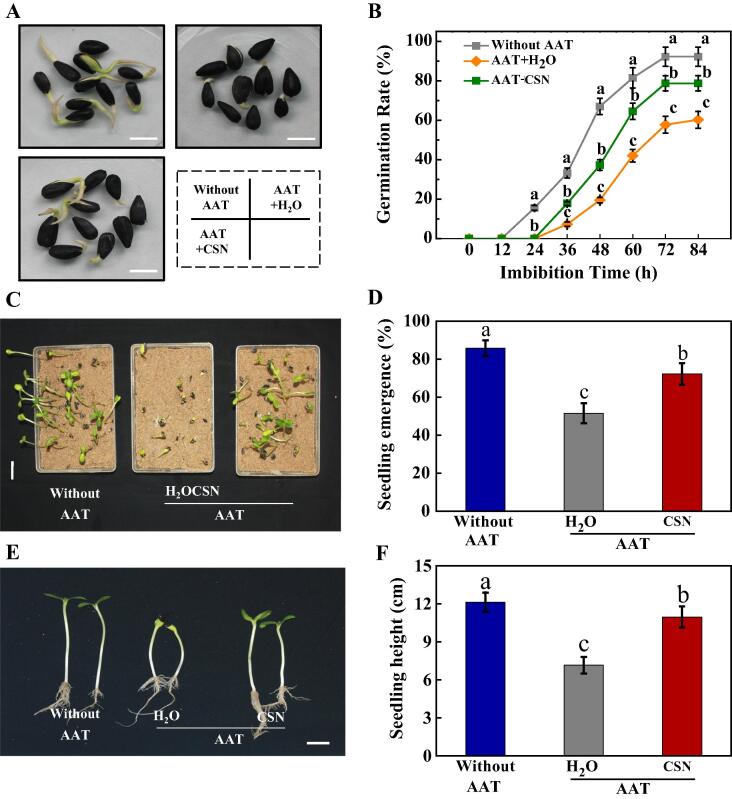
Fig.3.
CSN improved seed germination and seedling emergence of artificially aged sunflower seeds. (A) Typical images of different samples of sunflower seeds during imbibitions (48 h after sowing). Without AAT: healthy seeds without accelerated aging test (AAT); AAT + H2O: AAT seeds with H2O; AAT + CSN: AAT seeds with compound sodium nitrophenolate (CSN) treatment. Scale bar, 10 mm. (B) Time courses of germination rates of different samples (A) are presented. (C) Typical images of seedling emergence. Scale bar, 200 mm. (D) The seedling emergence rate for (C) was displayed. (E) Typical images of sunflower seeding height. Scale bar, 200 mm. (F) Quantitative analysis on the seedling height shown in (F). Four biological replicates each with 50 seeds for each treatment were set in seed germination and seedling emergence tests. The asterisk (*) or diverse lowercase(s) on top of the bars were indicative of significant differences (p < 0.01, Lsd) across treatments. Exogenous CSN at 25 mg·L−1 was employed.