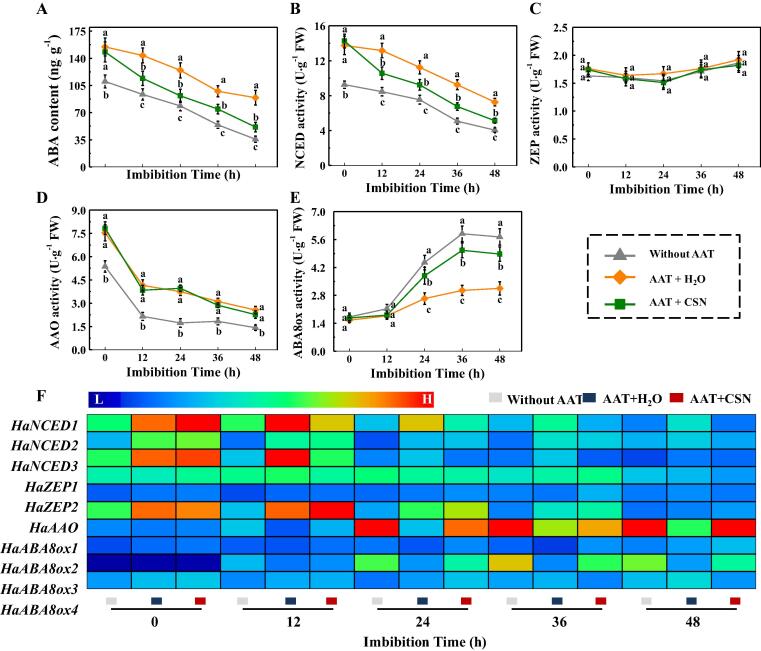
Fig. 8.
The effect of CSN on the abscisic acid (ABA) metabolism in sunflower seeds during imbibitions time. (A) ABA content. (B) 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase (NCED) activity. (C) Zeaxanthin epoxidase (ZEP) activity. (D) Abscisic acid aldehyde oxidase (AAO) activity. (E) Abscisic acid −8′-hydroxylases (ABA8ox) activity. (F) The transcriptional levels of ABA metabolism-related genes. Without AAT: healthy seeds without accelerated aging test (AAT); AAT + H2O: AAT seeds with H2O; AAT + CSN: AAT seeds with compound sodium nitrophenolate (CSN) treatment. Four biological replicates for each treatment were set in ABA determination and enzymes activity assay. Real-time quantitative PCR was performed using three biological replications, and each was made in three technical replicates. The asterisk (*) was indicative of significant differences (p < 0.01, Lsd) across treatments. Exogenous CSN at 25 mg·L−1 was employed. The Illustrator software was used for creating the heat map. The gene levels from low (L) to high (H) indicated the lowest and highest levels in the whole database.