Figure 1.
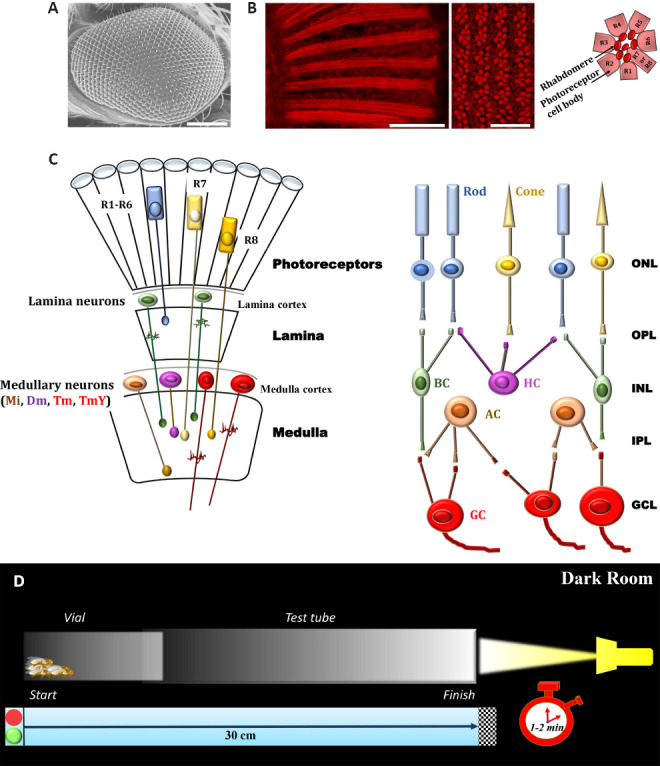
Basic structures underlying the early stages of visual processing of adult D. Melanogaster and experimental procedure for phototaxis assay.
(A) Scanning electron microscopy image of Drosophila eye (Oregon-R strain); scale bar: 100 µm (methods are in agreement with Catalani et al., 2021a, b). (B) Conventional (longitudinal section, left panel) and confocal (cross section, right panel) microscopy analysis of fly eyes stained with fluorescent phalloidin (F-actin staining) to detect rhabdomere morphology and the pattern of ommatidia/rhabdomeres, respectively (methods are in agreement with Catalani et al., 2021a, b). Scale bars: 20 μm (left) and 10 μm (right). Seven rhabdomeres are shown in any one given plane because R7 cell are placed atop the R8. The cartoon on the right depicts a transverse view of the ommatidial unit. Sourced from the authors’ unpublished data. (C) Schematic drawings of Drosophila (left) and vertebrate (right) retina. Main cell types are shown. Colored cells share similar functional characteristics. It should be noted that the complex retina (photoreceptor layer, ommatidial units)-lamina-medulla in flies is comparable to vertebrate retina circuitry in transfer of information through early stages of visual systems. (D) Experimental procedure to analyze the visual response of adult D. Melanogaster. A plastic vial (2.5 × 9.5 cm) is inserted and connected to a glass tube (3.0 × 23 cm) by transparent tape. The transparent apparatus (30 cm) is placed horizontal and perpendicular to the light source. The directional light source from one side, placed horizontal 15 cm away from the tube, acts as an attractant for the flies. In a dark room, flies are introduced independently in the apparatus and left separately for 30 minutes. This allow adaptation of the flies to darkness. The apparatus is then gently pounded down to place the flies at opposite end from the light. The light is then turned on and a timer started. A camera records fly behavior and their movement (horizontal walking) towards the light source during the experiment (1–2 minutes). Each trial was performed three times, at 1-minute intervals, and the results are averaged. Dm: Distal medulla intrinsic neurons; GCL: ganglion cell layer; INL: inner nuclear layer; IPL: inner plexiform layer; Mi: medulla intrinsic neurons; ONL: outer nuclear layer; OPL: outer plexiform layer; Tm and TmY: tangential medulla neurons (two classes, Tm neurons project to the lobula and TmY neurons to both the lobula and lobula plate).
