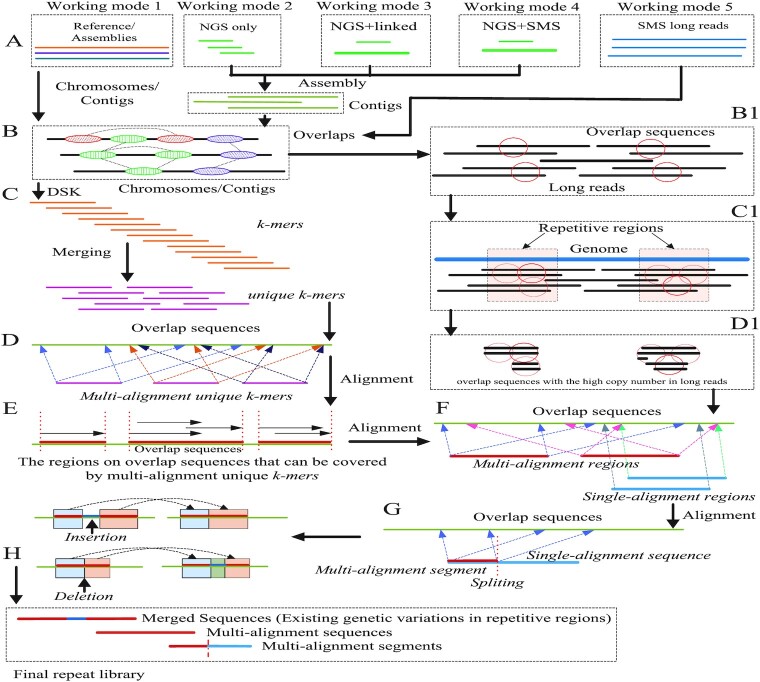
Figure 3.
The pipeline of LongRepMarker. (A) shows five working modes of LongRepMarker, which are reference-assisted mode, de novo mode based on only NGS short paired-end reads, de novo mode based on NGS short paired-end reads + barcode linked reads, de novo mode based on NGS short paired-end reads + SMS long reads and de novo mode based on only SMS long reads. (B) shows the principle of finding overlaps between chromosomes and contigs by using minimap2. (C) Transforming overlaps into unique k-mers by DSK. (D) Using minimap2 to obtain multi-alignment unique k-mers and the regions on chromosomes and contigs that can be covered by these unique k-mers. (E) Using minimap2 to obtain multi-alignment regions and single-alignment regions on chromosomes, contigs and long reads, and the sequences marked in multi-alignment regions are saved in the final repeat library. (F) Single-alignment regions are cut into several smaller segments, and some multi-alignment segments are saved in the final repeat library. (G) Analyzing the relationship and spacing between these saved sequences, combining some saved sequences and their gaps that meet certain conditions to a complete fragment and replacing the corresponding saved sequences in the final detection results by this fragment. (H) Components of the final repeat library. (A), (B), (B1), (C1), (D1), (F), (G) and (H) illustrate the workflow of the detection mode based on only the SMS long reads.