Figure 9.
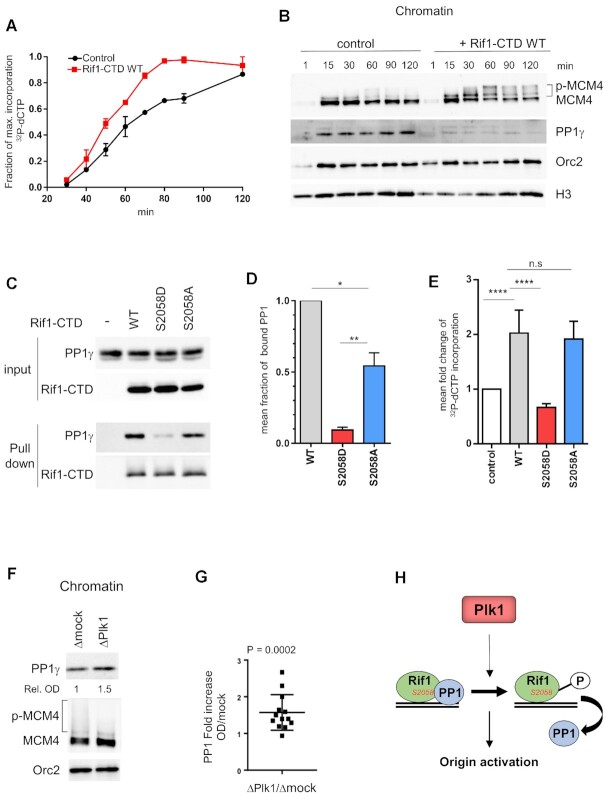
Rif1–CTD accelerates DNA replication dependent on PP1 interaction with Rif1-S2058. (A) Rif1–CTD or buffer was added to sperm nuclei (2000 nuclei/μl) replicating in egg extracts in the presence of [α 32P]-dCTP, DNA was purified at indicated times and replication was analyzed on alkaline gel electrophoresis, the mean incorporation with SEM from two independent experiments was plotted. (B) Rif1–CTD or buffer was added to sperm nuclei replicating in egg extracts, chromatin was purified at indicated times, specified proteins were analyzed by western blotting. (C) Buffer (-), wild type (WT), 1 μM Rif1–CTD mutants respectively (S2058D) and (S2058A) were added to egg extracts, recovered by pull-down after 1h incubation using Ni-magnetic beads, then analyzed by western blotting using anti-PP1 (PP1γ) or anti-Rif1 (Rif1–CTD) antibodies. (D) PP1 bound to Rif1–CTD was quantified, normalized to Rif1, and expressed as mean fraction with SEM of PP1 bound to WT Rif1–CTD in three independent experiments, unpaired or one sample t-test. (E) As in (A) WT, S2058D and S2058A Rif1–CTD were incubated in replicating reactions and [α 32P]-dCTP incorporation was quantified after DNA gel electrophoresis then plotted as mean fold increase compared to control (buffer) with SEM, in 3 (for WT, S2058D) or 5 (for WT, S2058A) independent experiments with different time points within (n = 9, n = 15 respectively), Mann-Whitney test. (F) Rif1–CTD or buffer was added to sperm nuclei (2000 nuclei/μl) replicating in mock- (Δmock), or Plk1- (ΔPlk1) depleted extracts, chromatin was purified after 60 min and indicated proteins were analyzed by western blotting. (G) Fold increase of chromatin bound PP1 normalized to Orc2 OD on western blots in Plk1- versus mock- depleted extracts from five different replication reactions with different time points, scatter dot blot with mean (n = 13), Wilcoxon signed ranked test, P-value above blot. (H) Model of Plk1 regulating origin activation via phosphorylation of Rif1 which interrupts the Rif1-PP1 interaction.