Figure 2. The acetyl CoA diversion pathway.
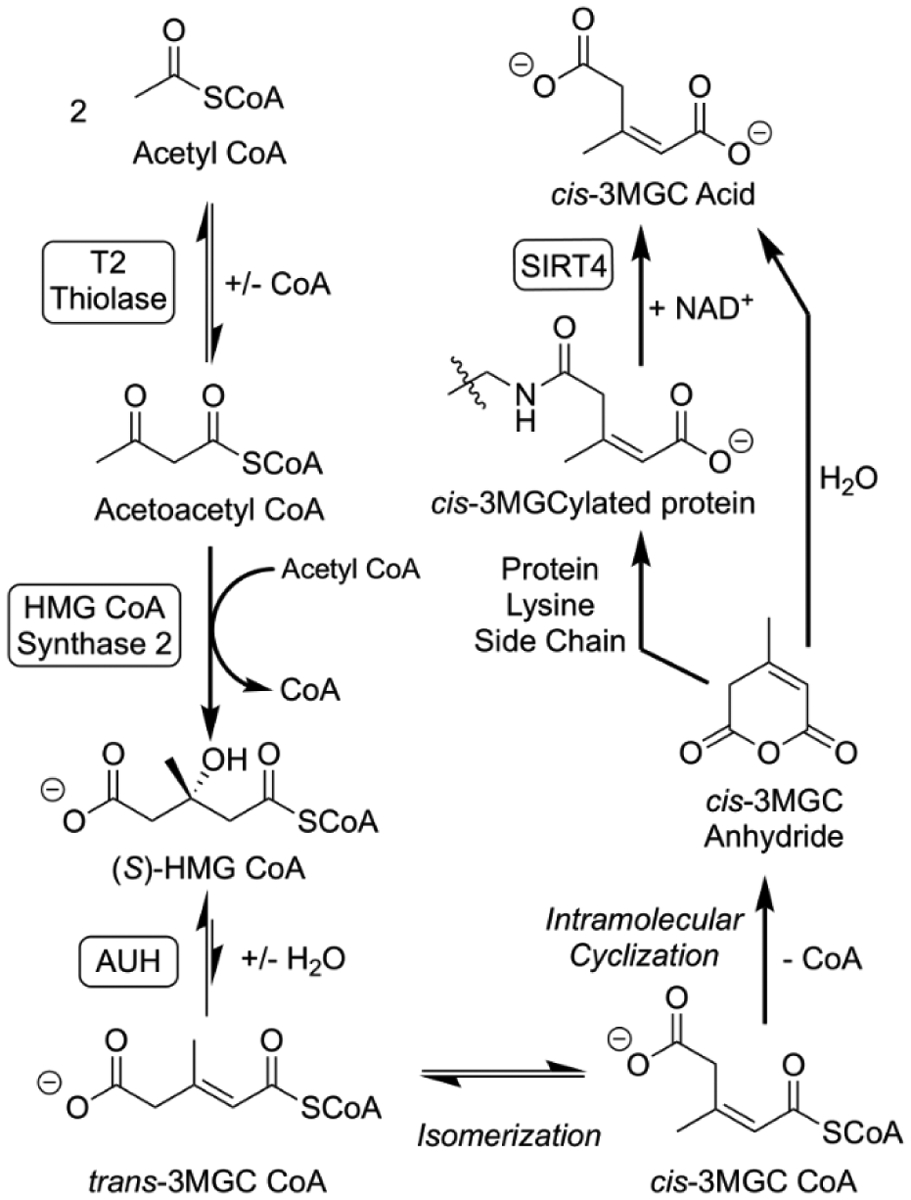
A sequence of three enzyme-mediated reactions that lead from acetyl CoA to to 3MGC CoA is depicted. Acetoacetyl CoA (T2) thiolase catalyzes the condensation of 2 acetyl CoA. Acetoacetyl CoA generated by this reaction reacts with another acetyl CoA in a second condensation reaction catalyzed by HMG CoA synthase 2. Subsequently AUH hydratase dehydrates HMG CoA to trans-3MGC CoA. Once formed, three non-enzymatic reactions follow, isomerization of trans-3MGC CoA to cis-3MGC CoA, intramolecular cyclization of cis-3MGC CoA to cis-3MGC anhydride, and hydrolysis to cis-3MGC acid. Alternatively, cis-3MGC anhydride can 3MGCylate protein lysine side chain amino groups. This latter product serves as a substrate for the NAD+-dependent deacylase, sirtuin 4 (SIRT4), which produces cis-3MGC acid as a reaction product.
