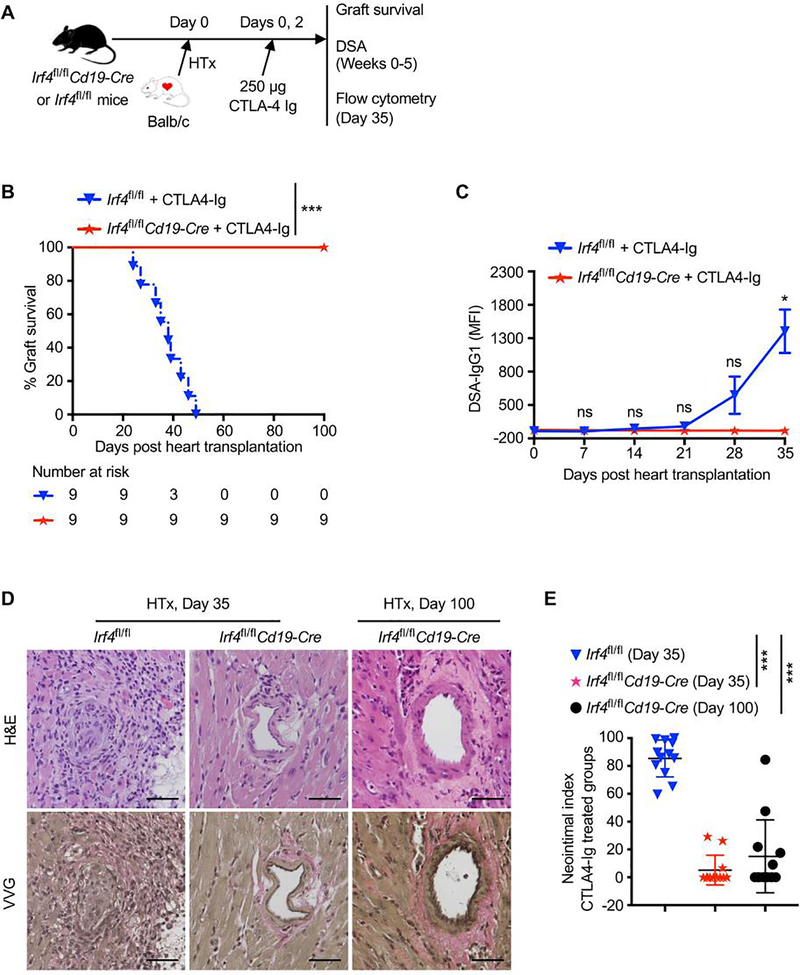
Figure 5. Deletion of IRF4 in B cells abrogates de novo DSA production and prevents chronic allograft rejection in CTLA4-Ig treated mice.
Irf4fl/fl control or Irf4fl/flCd19-Cre mice were transplanted with Balb/c hearts on day 0, and treated with 250 μg CTLA4-Ig on days 0 and 2. (A) Schematic of the experimental design. (B) % allograft survival after heart transplantation (HTx) (n = 9). ***P < 0.001 by log-rank test. (C) Serum samples were collected from transplant recipients at indicated days, and then incubated with Balb/c donor cells. The graph shows IgG1 MFI of CD45+ Balb/c donor cells. Data are shown as mean ± SD (n = 3) and are from one experiment that is representative of two independent experiments. ns, P > 0.05; *P < 0.05 by unpaired Student’s t test. (D and E) Heart allografts were harvested from CTLA4-Ig–treated groups at indicated days post-transplant. (D) Representative images show the H&E- and VVG-stained sections (x200 magnification) of heart allografts. Scale bars indicate 50 μm. (E) Morphometric quantification (neointimal index) of cardiac allograft vasculopathy. Arteries in VVG-stained sections (four grafts per group) were analyzed. ***P < 0.001 by unpaired Student’s t test.