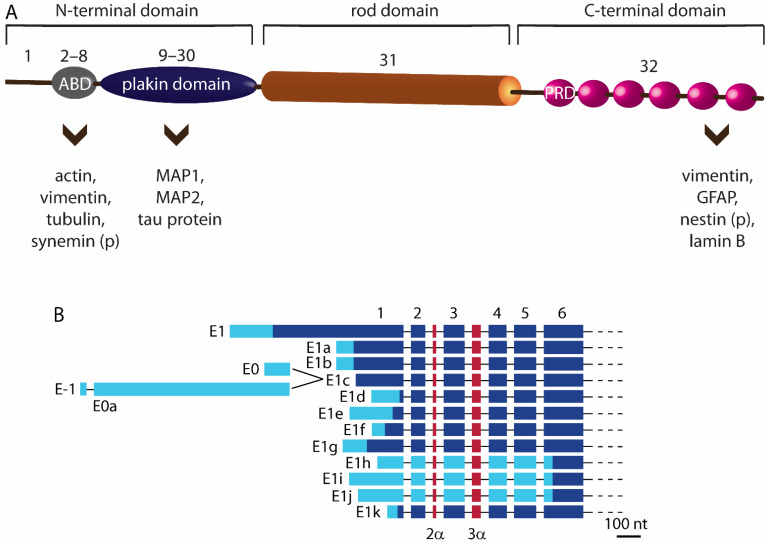
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of plectin and its transcripts generated by alternative splicing of the 5’ end of the plectin gene PLEC. (A) The panel highlights interaction sites of cytoskeleton proteins and/or their associated proteins in astrocytes and neurons with their respective plectin domains. The C-terminal domain consists of six plectin repeat domains (PRD). (p), predicted interaction sites of certain IFs with plectin in astrocytes and neurons. Numbers above the schematic of plectin denote exons. ABD, actin binding domain. (B) Transcripts that give rise to individual plectin isoforms differ from each other only in short sequences at the 5’ end of the plectin gene. The numbers above the schematic denote consequent exons until exon 6. Exons 7 to 32 are not shown, as they are conserved among isoforms [4]. Individual exons are indicated by light and dark blue boxes, representing noncoding and coding regions, respectively. Red boxes denote two optionally spliced exons; 2α is inserted between exons 2 and 3, while 3α is inserted between exons 3 and 4.