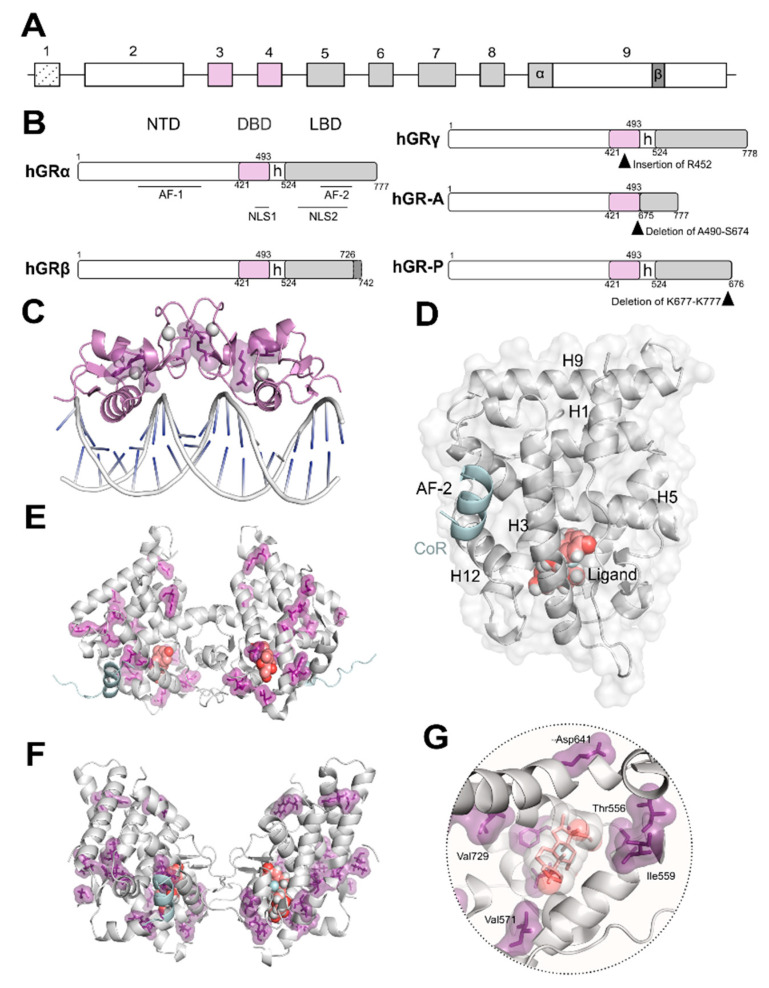
Figure 1.
Glucocorticoid receptor (GR) isoforms: domain organization and crystal structures. (A) Schematic representation of NR3C1/GR gene organization. A unique gene gives rise to several isoforms through alternative splicing (B) and/or alternative transcription initiation. The exons encoding for the modular domains: N-terminal domain (NTD), DNA-binding domain (DBD), and ligand-binding domain (LBD), are indicated; exon 9 encodes the two alternative C-termini of the LBD in GRα and GRβ. (B) Schematic representation of GR isoforms domain organization generated by alternative splicing. hGRα modular domains include the intrinsically disordered NTD harboring the ligand-independent activation function (AF)-1; the DBD, the most conserved along the nuclear receptor superfamily; a poorly conserved hinge region (h); and the LBD displaying the surface-exposed co-regulator AF-2 groove. The five splice variants GRα, GRβ, GRγ, GR-A, and GR-P are shown; insertion/deletions are indicated by black arrowheads. (C) Crystal structure of the GR-DBD dimer bound to DNA shown in grey cartoon (PDB code 5CBX). This domain can dimerize on (+)GRE to activate transcription. Residues implicated in glucocorticoid (GC) resistance are shown (V423, R469, R477, F478) in purple as sticks and surface. The zinc ions are shown as grey spheres. (D) Cartoon representation of the three-dimensional secondary structure of the GR-LBD monomer (PDB code 5UFS) and surface. The domain is depicted in standard orientation (i.e., with helices (H)1 and H3 displayed in the forefront and the AF-2 pocket, lined by H3, H5 and H12 on the left hand-side). The ligand is shown as salmon spheres and the co-regulator peptide (CoR) is shown in cyan. (E) Crystal structure of the first GR-LBD dimer reported (PDB code 1M2Z). The ligand is shown as salmon-coloured spheres and CoR is shown in cyan. Residues implicated in GC resistance are highlighted in purple (T556, I559, V571, V575, L595, D641, Y660, L672, G679, R714, H726, V729, F737, I747, I757, L773). (F) Crystal structure of a GR-LBD dimer reported (PDB code 5UFS) displaying a different self-recognition pose than in (E). The ligand is shown as salmon spheres and CoR is shown in cyan. Residues implicated in GC resistance (T556, I559, V571, V575, L595, D641, Y660, L672, G679, R714, H726, V729, F737, I747, I757, L773) are highlighted in purple. (G) Close-up of the ligand-binding pocket of GR occupied by the ligand dexamethasone shown in grey spheres and salmon sticks. Residues implicated in GC resistance contacting the ligand (T556, I559, V571, V729, F737, I747, I757) and lining the LBP are shown in purple.