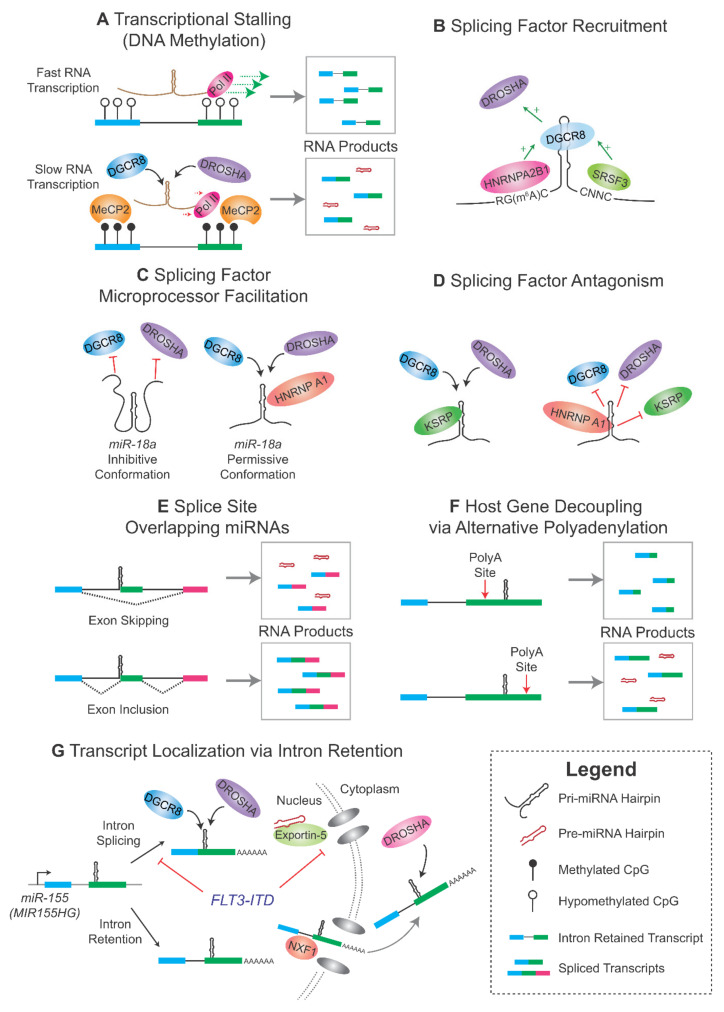
Figure 2.
Examples of Splicing Regulation of Intronic and Intragenic miRNAs. (A) Transcriptional stalling (as occurs due to DNA hypermethylation) promotes microprocessing of intronic miRNAs. (B) Splicing factor binding adjacent to miRNA hairpins promotes recruitment of DGCR8/DROSHA. (C) Splicing factor binding to miRNA hairpins can alter pri-miRNA accessibility to microprocessor binding. (D) Splicing factors compete for binding to miRNA hairpins to facilitate or hinder pri-miRNA microprocessing. (E) Inclusion of alternate exons inhibits the expression of splice site overlapping miRNAs. (F) Alternative polyadenylation decouples miRNA/host gene expression. (G) Intron retention modulates pri-miRNA localization. Refer to the text (Section 3) for details. Pol II = RNA Polymerase II; PolyA = polyadenylation.