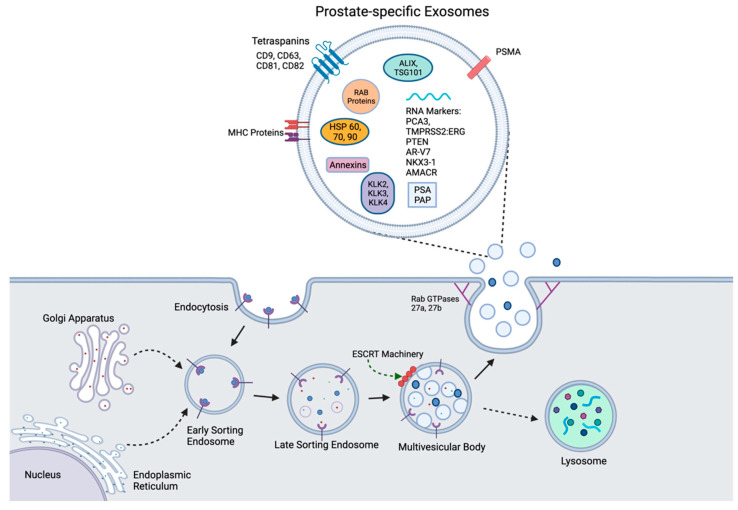
Figure 1.
Biogenesis of prostatic exosomes. Endocytosis via cell membrane invagination creates an early sorting endosome (ESE), which combines with other ESEs from the Golgi apparatus and the endoplasmic reticulum to create a late sorting endosome (LSE). Via ESCRT-dependent or ESCRT-independent mechanisms, further invagination creates ILVs within a multivesicular body (MVB). The MVB may either be shuttled to a lysosome for degradation or to the cell surface with the help of MVB docking proteins, such as Rab GTPases 27a and b, to expel its contents, including exosomes, out of the cell. Prostate-specific exosomes (top) contain nonspecific exosome biomarkers, such as heat shock proteins and tetraspanins, while also including kallikreins, PSMA, PCA3, and TMPRSS2:ERG, which are specific to exosomes of prostatic origin.