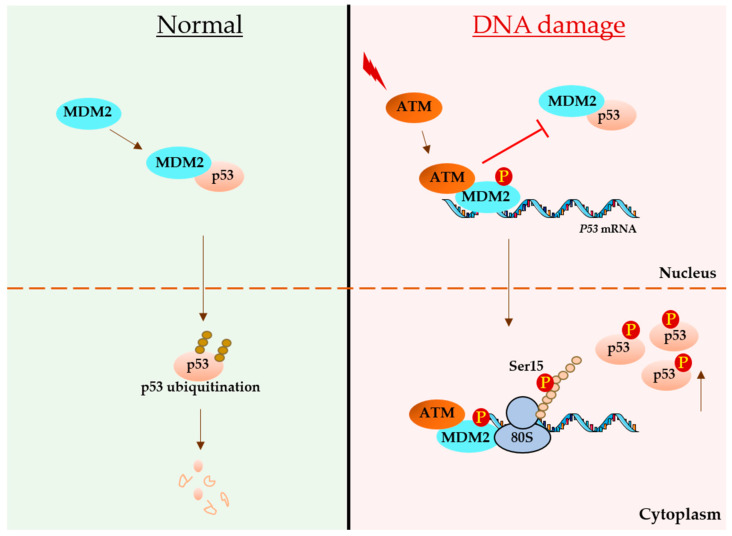
Figure 2.
MDM2 switches p53 regulation during DNA damage. Under normal conditions, the MDM2 protein interacts with the p53 protein in the nucleus and tags it for ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation, thereby keeping the p53 levels at minimum. Upon DNA damage, this negative regulation switches to the positive mode. The ATM kinase phosphorylates MDM2 at serine 395, and this allows MDM2 to interact with p53 mRNA and stimulate its translation. MDM2 also brings ATM to p53 polysomes and phosphorylates the nascent p53 peptide at serine 15, and this phosphorylation prevents MDM2-mediated p53 protein degradation.