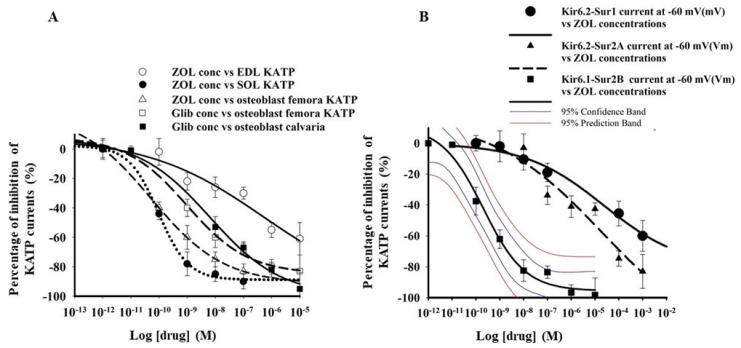
Figure 2.
Concentration-response relationships of zoledronic acid (ZOL) against KATP currents of native tissues and the currents of recombinant subunits expressed in Hek293 cells. (A) A significant leftward shift of the curves was observed in Soleus (SOL) and primary long bone cells in the presence of an increasing concentration of ZOL on the log x-axis, indicating that the drug potently inhibited the channel subunits in these tissues. Glibenclamide (Glib) potently inhibited the KATP currents of primary long bone cells and calvaria bone cells. The percentage of inhibition of the currents caused by ZOL was calculated against the current recorded at −60 mV (Vm) in the presence of ATP 5 × 10−3 M in excised macro patches and BaCl2 in C-A patches −60 mV (ΔVm). The data point represents the mean ± E.S. of a minimum of 13 patches/cells/fibers. (B) A significant leftward shift of the concentration-response curves of the KIR6.1-SUR2B current subunits was observed in the presence of the increasing concentration of ZOL on the log axis. The percentage inhibition of the currents caused by ZOL was calculated against the current recorded in whole cells at −60 mV (Vm) in physiological conditions in the presence of BaCl2. The data point represents the mean ± E.S. of a minimum of 15 cells.