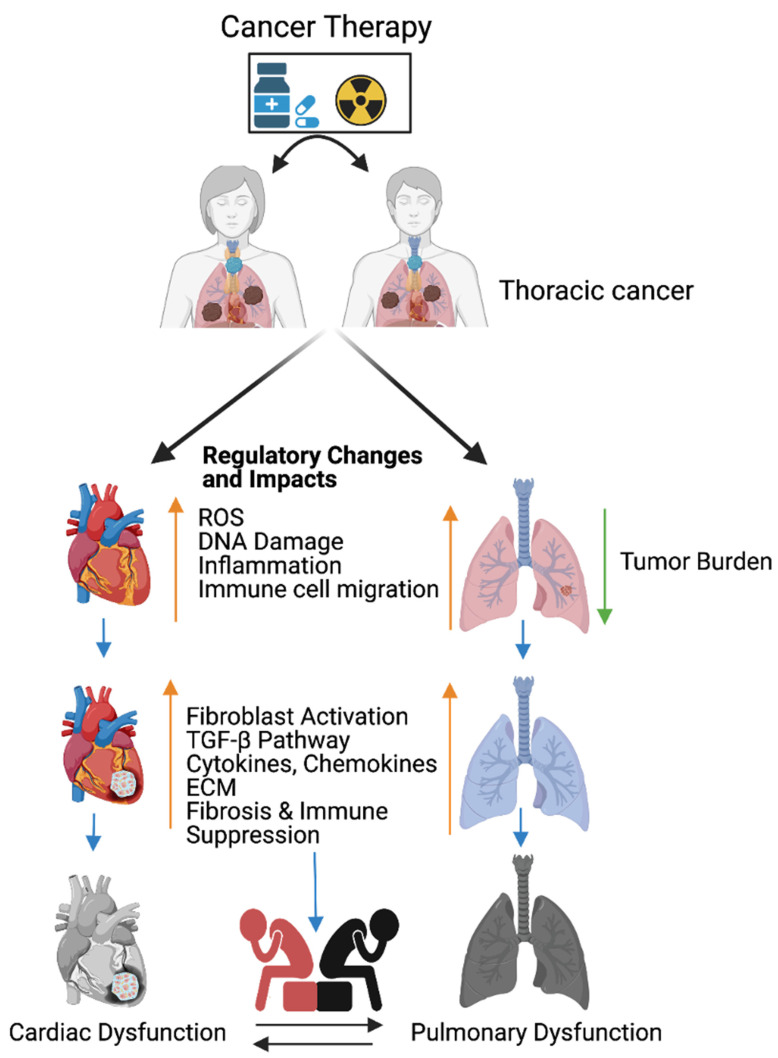
Figure 1.
Cancer therapy-induced cardiopulmonary failure. Cartoon illustrates the combination of chemotherapy and ionizing radiation promotes reactive oxygen species (ROS) in thoracic cancer (lung) patients. ROS promotes oxidative stress, DNA damage, immune cell migration, and inflammation, and reduces lung tumor burden. Immune cells at wounded sites secret cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors in cardiopulmonary tissue. Cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors activate myofibroblasts, promote the TGFB pathway, and are involved in the accumulation of the extracellular matrix (ECM). Accumulation of excess ECM induces cardiopulmonary fibrosis, tissue remodeling, immune escape, and cardiopulmonary failure in cancer-free male and female patients who received cancer therapy (chemoradiation therapy). Up arrow indicates the indicated process and the down arrow indicates the reduced tumor burden. This graphic/cartoon is created with BioRender.com agreement # IP22YQRECH.