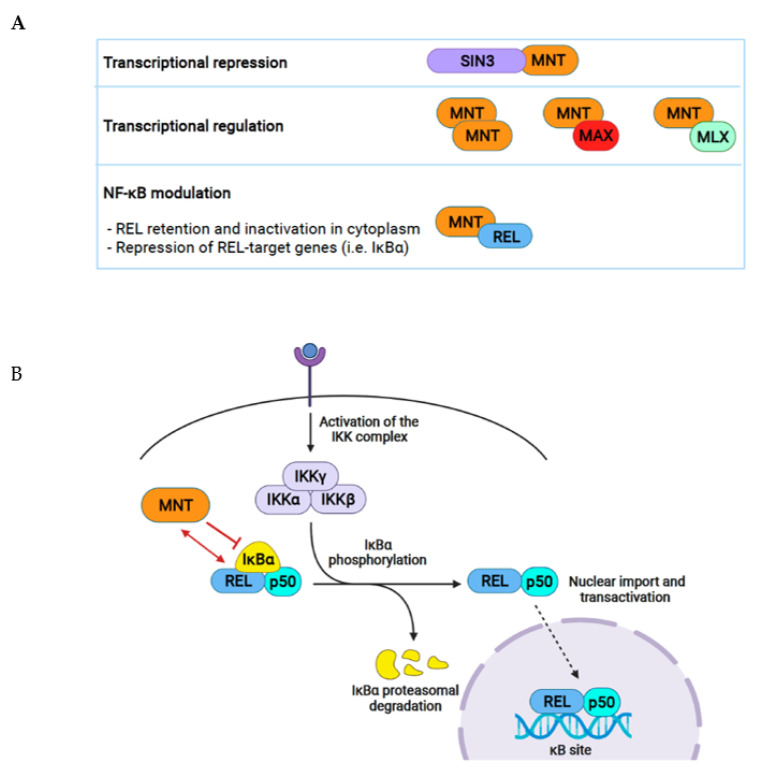
Figure 4.
MNT functional interactions. (A) MNT represses transcription through SIN3, which recruits a HDAC complex and turns DNA into a closed conformation. MNT homodimers and MNT–MAX and MNT–MLX heterodimers regulate transcription by binding DNA at E-boxes. MNT–REL interaction results in NF-κB regulation by retaining REL dimers inactive in the cytoplasm and by repressing REL target genes that would usually be activated by REL. (B) Once the cell receives an NF-κB activation signal, the IKK complex is activated and is able to phosphorylate IκBα, which is bound to REL-p50 dimers in the cytoplasm. This phosphorylation targets IκBα for ubiquitination and posterior proteasomal degradation. Finally, the REL-p50 dimers are free to translocate into the nucleus and regulate their target genes by binding to κB sites on the DNA. MNT forms complexes with REL and inhibits its functions.