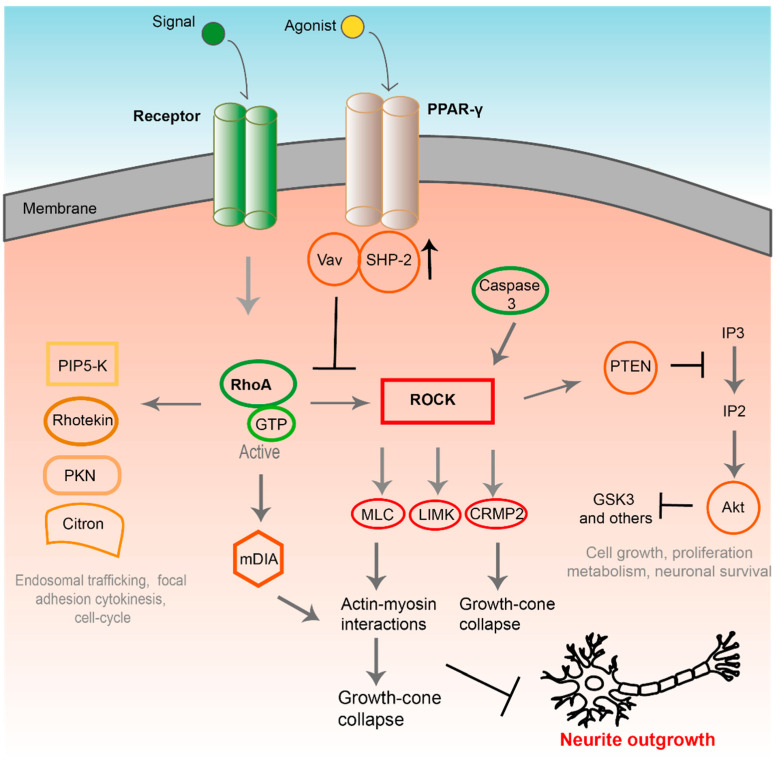
Figure 2.
PPAR-γ receptor and its effect on downstream pathways that are potential targets for drug agents. Including the Rho/ROCK inhibitory pathway which when blocked stops growth-cone collapse and encourages neurite outgrowth. Proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR-γ), Src homology region 2–containing protein tyrosine phosphatase-2 (SHP-2), Ras homolog family member A (RhoA), guanosin-5′-triphosphate (GTP), phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate-5 kinase (PIP5K), protein kinase N (PKN), Rho-associated kinase (ROCK), myosin light chain (MLC), LIM kinase (LIMK) and collapsin response mediator protein 2 (CRMP2), phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN), inositol triphosphate (IP3), inositol biphosphate (IP2), serine/threonine protein kinase B (Akt) [19].