Figure 2.
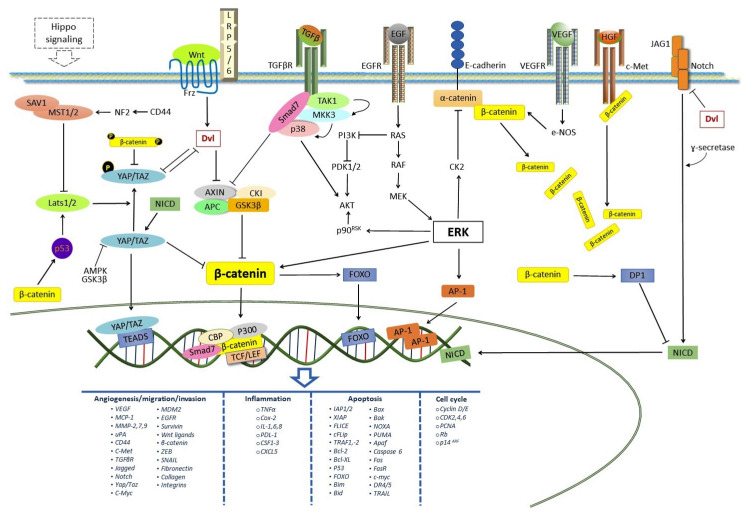
The crosstalk of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway with the Hippo, TGFβ, EGFR, VEGF, c-Met, and Notch signaling pathways modulates cancer progression and apoptosis, depending on the cellular context. An activation of the canonical Wnt pathway induces the stability of cytoplasmic β-catenin when the Wnt ligand binds FZ/Lrp5/6. This leads to a phosphorylation of Dvl, which inactivates the Destruction Complex, allowing an increase in the levels of free cytoplasmic β-catenin, which is then translocated to the nucleus, bound to TCF/LEF and transcription activators, to induce genic expression. On the other hand, the Hippo signaling increases β-catenin cytoplasmic levels by inactivating YAP/TAZ via SAV/MST1/2/LATS 1/2. When phosphorylated, YAP/TAZ activates the destruction complex via Dvl inhibition and sequestration of β-catenin. However, β-catenin also inhibits YAP/TAZ via Dvl and proteasomal activity, blocking the genic expression induced by YAP/TAZ. The Hippo signaling is activated via CD44/NF2 and p53. The TGFβ signaling pathway can also induce the cytoplasmic stability of β-catenin through smad 7. In turn, smad 7 interacts with TAK1 and MKK3, leading to the activation of p38 and the subsequent activation of AKT, inactivation of GSK 3β, and stabilization of β-catenin. The EGF pathway also can induce an increase in free cytoplasmic β-catenin by promoting the phosphorylation (inactivation) of α-catenin bound to E-cadherin through ERK activation. The VEGFR pathway also can increase the cytoplasmic levels of β-catenin through eNOS activation, which induces the S-nitrosylation of β-catenin, promoting its dissociation from α-catenin and its nuclear translocation. In addition, after the HGF ligand binds its receptor, c-MET promotes the phosphorylation of c-Met-associated β-catenin and a subsequent release of free cytoplasmic β-catenin. However, the activation of the Notch pathway by its Jagger ligand can decrease the cytoplasmic levels of β-catenin through the induction of DKK and Yap/Taz transcripts, which inhibit the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Conversely, the Wnt/β-catenin pathway inhibits the Notch pathway through Dvl and DP1. Additionally, β-catenin induces the activation of the pro-apoptotic transcriptional factor FOXO. Depending on the cellular context, this could lead either to a carcinogenic process or a cell death process on cancer cells. Continue arrows (↓) indicate activation, arrows with (⊥) indicate inhibition.