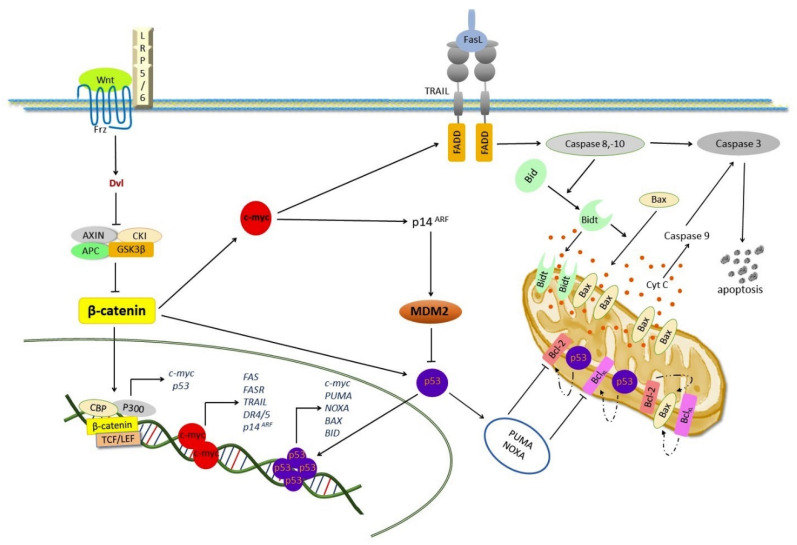
Figure 4.
Suggested pathway initiated by β-catenin to promote the induction of apoptotic cell death on cancer cells. β-catenin can be stabilized by the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and/or the EGF and TGF-β signaling pathways. β-catenin can bind and activate TCF4/LEF, which may activate the transcription of p53 and c-myc. C-myc can increase the genic expression of p14ARF, fas, Trail, fasR, and DR4/5. FasR and DR4/5 activate the apoptotic extrinsic pathway, which is initiated by the binding of their respective ligands. This leads to the autoactivation of caspases-8 and -10, which in turn promote the catalytic activation of the effector caspase-3. Another target of caspase-8 is the pro-apoptotic protein Bid, which is hydrolyzed to tBid, inducing Bax oligomerization and mitochondrial depolarization with release of cyt c. Along with the activation of caspase-9, these events amplify the apoptotic pathway. On the other hand, p14ARF inhibits mdm2, which induces the ubiquitination and ensuing degradation of p53. p53 can induce apoptosis via transactivation of pro-apoptotic genes such as Noxa, Puma, Bax, and Bid, which inhibit the Bcl-2 and BclXL anti-apoptotic proteins. p53 also acts by directly inhibiting BclXL and Bcl-2 in the mitochondria, inducing the permeabilization of the mitochondrial outer membrane, with the ensuing release of cyt c y the activation of apoptosis intrinsic pathway. Furthermore, p53 induces c-myc genic expression. Continue arrows (↓) indicate activation, arrows with (⊥) indicate inhibition.