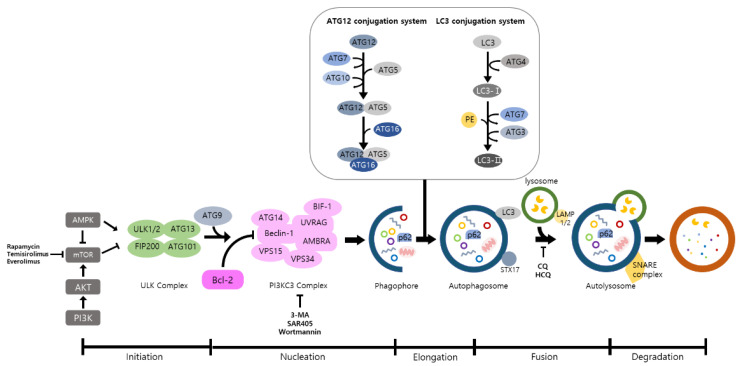
Figure 1.
The overall autophagic process and the inhibitors targeting each step. Autophagy includes a multistep procedure: (1) initiation, (2) nucleation, (3) elongation, (4) fusion, and (5) degradation. AMPK and mTOR are major modulators of autophagy and ATGs are deeply associated with this procedure. When the autophagic process is initiated, ULK phosphorylates ATG13 and FIP200 are activated. In nucleation, ULK1 phosphorylates Ambra1, which interacts with Beclin-1, and Beclin-1 forms a PI3KC3 complex with other proteins. After that, cytoplasmic components are enclosed by the phagophore that is expanded to form autophagosomes. These double membranes are fused with lysosomes to form autolysosomes, and various cytoplasmic components are degraded by several enzymes in the autolysosomes. (AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; mTOR: mammalian target of rapamycin; ATG: autophagy related gene; ULK: Unc-51 like kinase; FIP200: Focal adhesion kinase family interacting protein of 200-kDa; PI3KC3: Class III phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase).