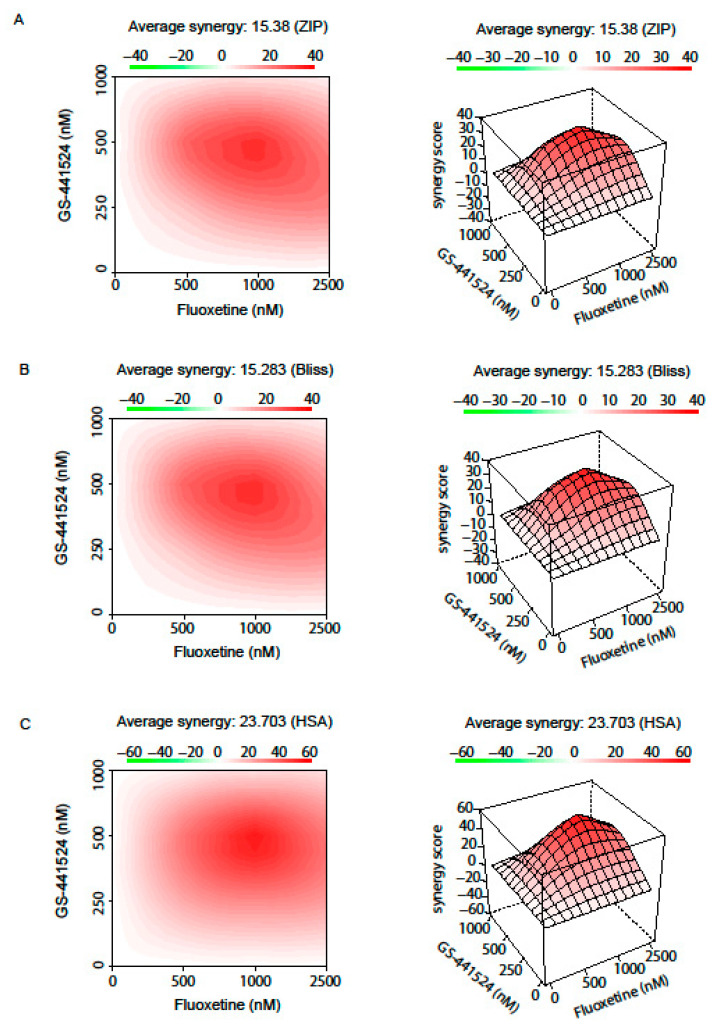
Figure 4.
Pharmacological interaction profile of the drug pair GS-441524 and fluoxetine. Drug interactions were analyzed based on the three commonly used reference models: (A) Zero Interaction Potency (ZIP), (B) Bliss independence, and (C) highest single agent (HSA). While the HSA model assumes a synergistic drug combination that produce additional benefits on top of what the drugs can achieve alone, the Bliss independence model uses probabilistic theory to model the effects of individual drugs in a combination as independent yet competing events. Synergy calculations via the ZIP model includes the comparison of potency changes of the dose–response curves between individual drugs and their combinations. A color-coded interaction surface was used to illustrate the synergy scores of the responses, where high synergistic scores are colored in red. Synergy score calculations via the ZIP and Bliss independence model revealed a synergy of ~ 15, while the HSA model showed a higher synergy score of ~23.