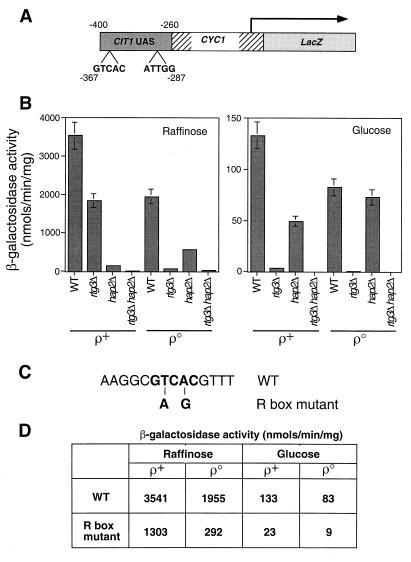
FIG. 3.
A functional R box in the CIT1 UAS. (A) Diagram of a CIT1 UAS-CYC1-lacZ construct in which a 140-bp fragment of the upstream region of CIT1 from bp −400 to −260 was fused to the transcriptional start site of the CYC1 gene and fused to the reading frame of the E. coli lacZ gene. Positions of the putative Rtg1p-Rtg3p R box binding site, GTCAC, and the Hap2,3,4,5p binding site, ATTGG, are indicated. (B) Wild-type (WT) PSY142 [rho+] and [rho0] cells and rtg3Δ, hap2Δ, and rtg3Δ hap2Δ derivatives were transformed with the CIT1 UAS-CYC1-lacZ construct in a centromeric plasmid. Pools of 10 transformants of each were grown to mid-log phase on YNBcasR or YNBcas5%D medium, and β-galactosidase activity was determined in cell-free extracts. (C) Two mutations were introduced into the R box in the CIT1 UAS-CYC1-lacZ construct as indicated in boldface and described in Materials and Methods. This construct was placed into a centromeric plasmid to yield pCIT1(R)(UAS)-CYC1-LacZ. (D) PSY142 [rho+] and [rho0] cells were transformed either with pCIT1(UAS)-CYC1-LacZ, containing the wild-type R box, or with pCIT1(R)(UAS)-CYC1-LacZ, containing the mutant R box construct. Ten transformants of each were pooled and grown to mid-log phase in YNBcasR or YNBcas5%D medium, and β-galactosidase activities were measured in cell-free extracts. Standard errors from triplicate assays are <10%.