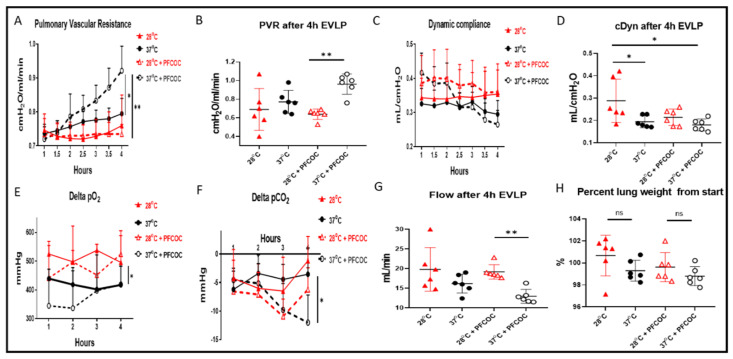
Figure 1.
Lung oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange function, PVR, Cdyn and flow during EVLP. (A). PVR values during EVLP at 37 °C +/− PFCOC were higher than the subnormothermic conditions but only significantly higher when compared to EVLP at 28 °C with PFCOC (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01). During the 5 min end of EVLP stress test, (B) the PVR in the 28 °C + PFCOC EVLP was significantly reduced (** p < 0.01) but the similar variations observed at 28 °C without PFCOC were not significant when compared to EVLP at 37 °C without PFCOC. (C). Cdyn values during EVLP at 28 °C +/− PFCOC were higher but not significantly higher than the EVLP at 37 °C +/− PFCOC. During the 5 min end of EVLP stress test, (D) the Cdyn of the 28 °C without PFCOC was significantly higher than the 37 °C temperature (* p < 0.05). (E). During EVLP at 28 °C +/− PFCOC, the lung oxygen exchange function was higher when compared to the 37 °C +/− PFCOC conditions (* p < 0.05). (F). During EVLP at 37 °C + PFCOC condition the lung carbon dioxide exchange function were significantly higher as compared to the 37 °C without PFCOC condition (* p < 0.05). (G). During the 5 min end of EVLP stress test, in the 28 °C + PFCOC EVLP, the flow was significantly higher (** p < 0.01) compared to EVLP at 37 °C with PFCOC. (H). The lungs gained weight after EVLP at 28 °C +/− PFCOC but weight gains were not significantly higher when compared to the 37 °C +/− PFCOC conditions.