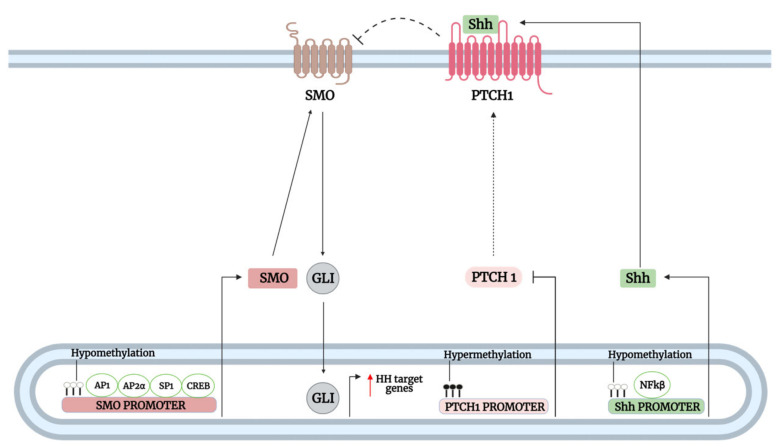
Figure 5.
A simplified illustration of SMO-dependent GLI regulation in the context of transcriptional regulation. The binding of transcription factors AP1, AP2α, SP1, and CREB to promoter regions of SMO kickstarts the onset of its transcription. Similarly, the binding of NFκB to the NFκB binding site located within the Shh promoter induced the transcriptional upregulation of Shh. Furthermore, the increased transcriptional output of SMO and Shh can also occur as epigenetic events through hypomethylation of CpG islands that reside within promoters, which further promotes the binding of transcriptional machinery to promoters. Conversely, hypermethylation of the PTCH1 promoter leads to decreased transcriptional expression and consequently decreased production of PTCH1 protein. Together, these molecular events work in concert to further enhanced Hh pathway activity and promote tumorigenesis. Dotted triangle-headed arrow: inactivated function; dotted bar-headed arrow: loss of inhibition; red upward triangle-headed arrow: upregulation.