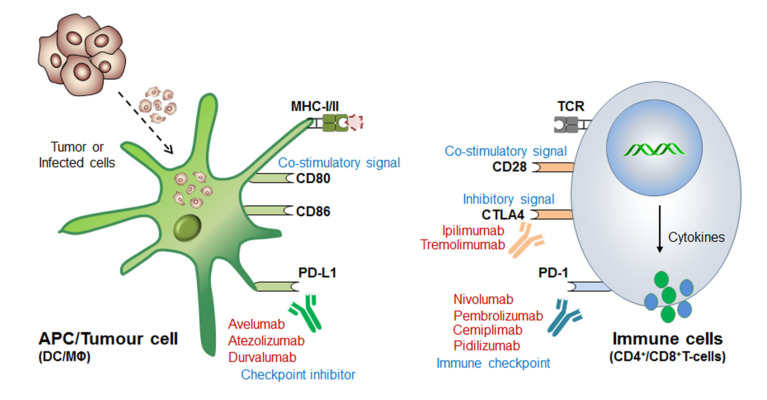
Figure 2.
Mechanism of immune checkpoint blockage or inhibition (ICB/ICI) therapy. The antigen presenting cells (APCs), especially dendritic cells and macrophages recognize and engulf the virus-infected or cancerous cells. The immune cells now processed and present the antigen to the naive T-cells in conjugation with MHC-I/II. The T-cell receptor (TCR) present on the immune cells recognizes this processed antigen and activates humoral as well as cell-mediated immune response. However, interestingly, immune cells, like CD8+T-cells also express PD-1 marker which function as “immune checkpoint” before cytolytic activation. On the other hand, tumor-engulfed DCs also expresses PD-L1 and PD-L2 (ligand for PD-1) and inhibitor bypass the function of immune activation called “immune checkpoint inhibitor” and thus T-cells filed to recognize it and considered as ‘self’ rather than ‘foreign’. Therefore tumor cell escapes this immune-surveillance mechanism and proliferates rapidly. Blocking these immune checkpoint markers by means of specific antibodies endorsed the discovery of ICB-therapeutics, for example, (i) Anti-PD-1 therapy (or Immune cell targeted therapy): Nivolumab (Opdivo®), Pembrolizumab (Keytruda®), Pedilizumab (CT-011) and Cemiplimab (Libtayo®) block PD-1 receptor and bypass the ‘self-recognition’ mechanism of T-cells, and thereby allowing rapid recognition and cytolytic activation to kill tumor cells. (ii) Anti-CTLA4 therapy: Immune cell (T-cells) expresses CTLA-4 to maintain normal homeostasis by regulating the hyper activation of other immune cells and also to avoid autoimmunity, just like ‘speed breaker’. But due to its impairments under the TME it is required to be constantly activated, and so anti-CTLA4 antibodies, like Ipilimumab (Yervoy®) and Tremolimumab efficiently block the inhibitory effect of CTLA-4. Moreover, since it is highly homologous to CD28-receptor functions, thereby further activating CD8+T effector function to enhance anti-tumor immunity. (iii) Tumor targeted therapy (or, immune checkpoint inhibitor): The anti-PD-L1 antibodies, like Atezolizumab (Tecentriq®), Avelumab (Bavencio®) and Durvalumab (Imfinzi®) blocks the inhibitory signal generated by tumor expressing PD-L1 (ligand for PD-1) to stop its self-defense mechanism, resulting in rapid tumor killing by T-cell attack. The detail mechanism of antigen presentation, ICB-therapy and strategies to overcome drug-resistance is well discribed in these articles [64,75].