Figure 5.
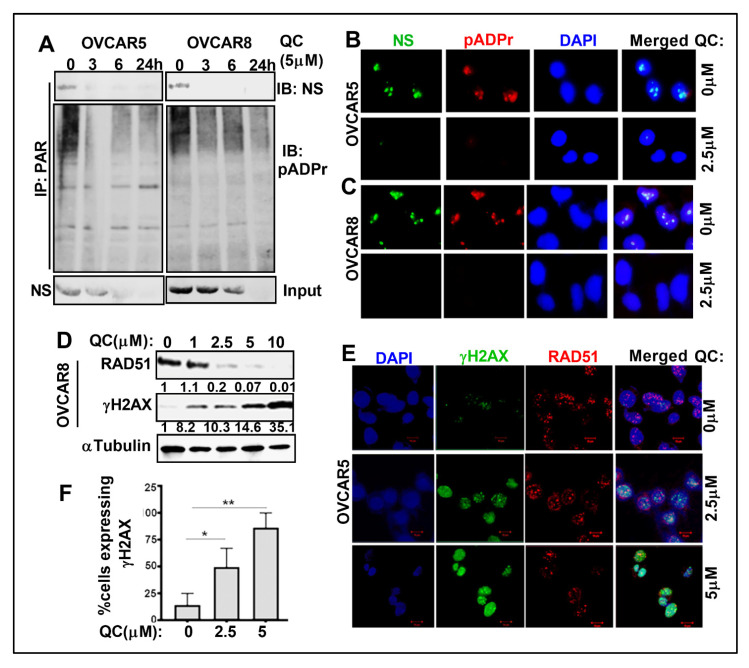
QC downregulates NS PARylation. and induces DNA damage. (A) OVCAR5 and 8 cell extracts were immunoprecipitated with anti-PAR antibody from untreated and QC-treated cells and probed for NS PARylation levels in a time dependent manner. (B) IF analysis shows NS (green) and pADPr (Red) colocalizes with each other (Merged image) and DAPI was used to stain the nuclei in OVCAR5 and (C) OVCAR8 cells. (D) Western analysis was performed in OVCAR8 cells to show the dose dependent increase in γH2AX levels and concomitant reduction in RAD51 levels upon QC treatment. αTubulin was used aa loading control. Densitometric analysis was performed using Image J, normalized and fold change was provided beneath the panel. (E) Representative IFC images of OVCAR5 cells untreated and treated with 2.5 and 5.0 µM QC showing γH2AX (green) and RAD51 (Red). DAPI-stained nuclei are in blue. (F) Quantitation of γH2AX levels. The number of cell nuclei displaying <5 foci (negative), between 6 and >20 foci, and diffuse pan-nuclear staining for pH2AX and RAD51 foci was quantified. At least 50 cells were counted (×40) for drug treatment per experiment. * (p < 0.05), ** (p < 0.01). Abbreviations: QC: Quinacrine; NS: Nucleostemin; IP/IB: immunoprecipitation/immunoblot; PAR: protein-conjugated polymers of ADP-ribose; pADPr: Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymer; H2AX: H2A histone family member X.