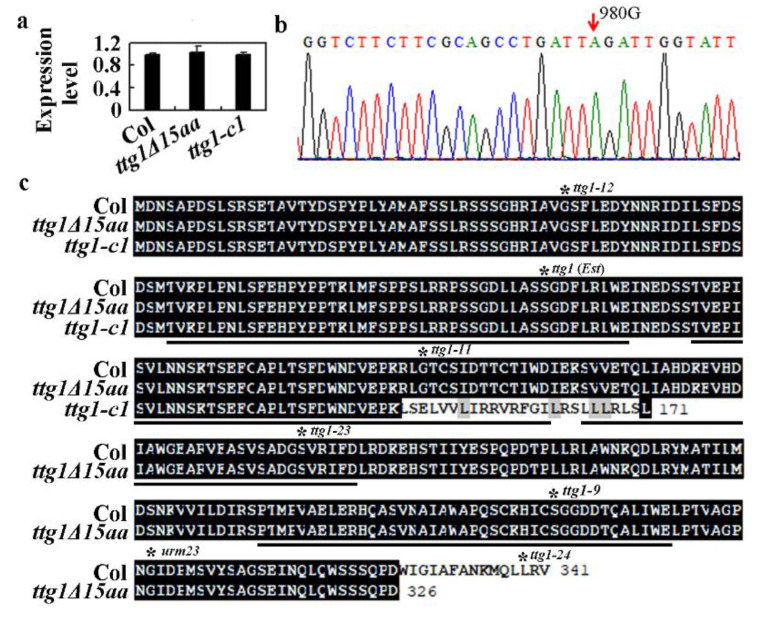
Figure 2.
A single nucleotide substation in TTG1 led to premature stop in the ttg1Δ15aa mutant. (a) Expression of TTG1 in the Col wild type, the ttg1Δ15aa, and the ttg1-c1 mutants. RNA was isolated from 10-day-old seedlings, and qRT-PCR was used to examine the expression of TTG1. The expression of ACT2 was used as an inner control, and the expression level of TTG1 in the Col wild type was set as 1. Data represent the mean ± SD of three replicates. (b) Sequence of TTG1 in the ttg1Δ15aa mutant. The arrow indicates the 980G-A single-base substitution. (c) Amino acid alignment of TTG1 in the Col wild type, the ttg1Δ15aa, and the ttg1-c1 mutants. ORFs of TTG1 in the ttg1Δ15aa and the ttg1-c1 mutants were identified by using DNAMAN, and the predicted full-length amino acid sequences were used for alignment with the full-length amino acid sequence of TTG1 in the Col wild type. The numbers at the C-terminal indicate the numbers of total amino acids of TTG1 in the Col wild type, the ttg1Δ15aa, and the ttg1-c1 mutants. Solid underlines indicate the WD40 domains. Stars indicate the amino acids that were substituted in the corresponding mutants as summarized previously [2].