Fig. 4.
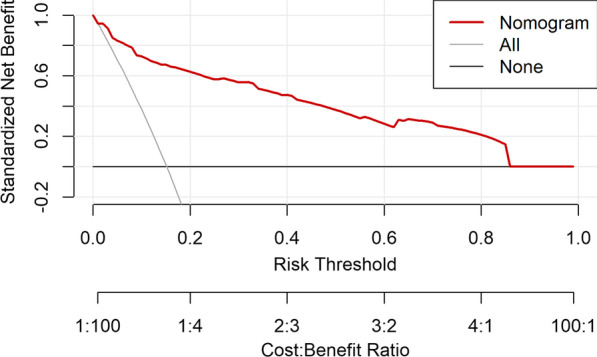
Decision curve analysis of the nomogram predicting the risk of ICU need in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. The x-axis indicates the threshold probability, y-axis measures net benefit by adding true positive and subtracting false positive. A low-risk threshold probability might indicate that delaying the ICU admission is far more harmful than early admission; a higher threshold might indicate that waiting the parameters to reach critical levels is relatively more harmful than unnecessary ICU admission. When, threshold probability between 0.15–0.85, predicting ICU admission by using our nomogram model would provide higher benefit than the admitting all the patients to the ICU (All i.e. treat all) or admitting none of the patients to the ICU (None i.e. treat none)
