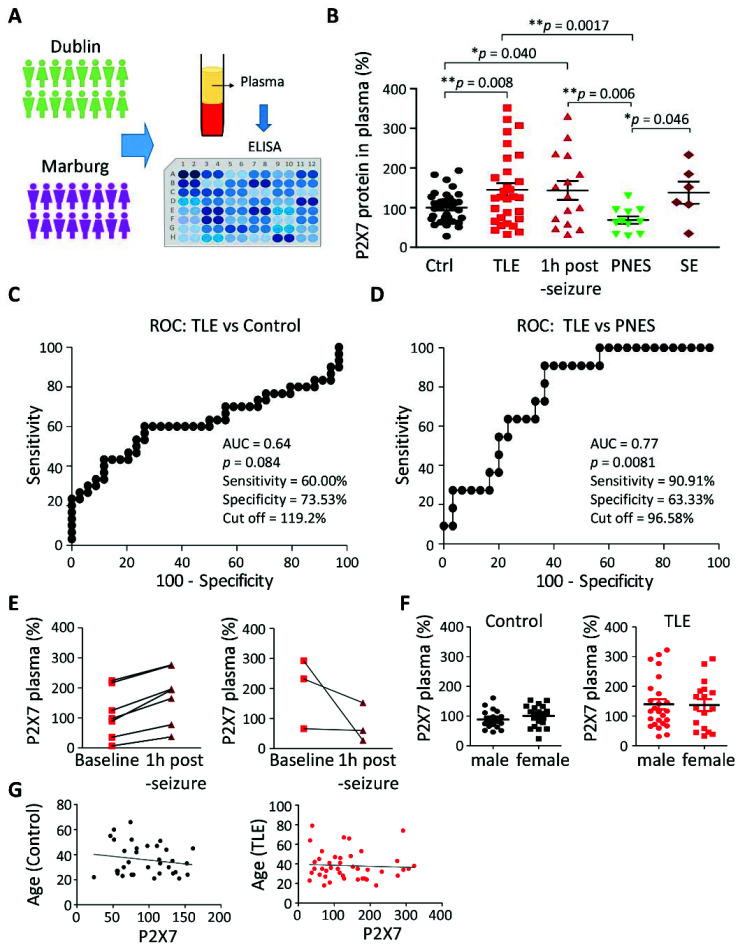
Figure 1.
Increased P2X7R protein levels in plasma of patients with TLE. (A) Patients were recruited from two hospitals: Marburg Hospital (Germany) and Beaumont Hospital (Ireland), and plasma samples were analyzed via P2X7R-detecting ELISA. (B) Bar chart showing P2X7R protein levels in plasma from temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) patients (N = 30) in baseline conditions and 1 h post-seizure (N = 15) are higher when compared with healthy controls (Ctrl) (N = 34) and patients with psychogenic non-epileptic seizures (PNES) (N = 11). In addition, P2X7R protein levels were also higher in patients suffering from an episode of status epilepticus (SE) (N = 6) when compared with PNES patients. ANOVA with post-hoc Fisher correction. Data are given as percentage to control. (C) ROC curve analysis shows P2X7R plasma levels have a moderate sensitivity (60%) and good specificity (74%) for discriminating between healthy controls and TLE patients with an AUC of 0.64 at a cut-off of 119.2%. (D) ROC curve analysis demonstrating a good sensitivity (90%) and specificity (63%) for discriminating between TLE patients and patients with PNES with an AUC of 0.77 at a cut-off of 96.58%. (E) Dot plot showing P2X7R plasma levels in the same patients at baseline and 1 h post-seizure. Out of 10 patients, 7 showed increased P2X7R in plasma and 3 lower P2X7R plasma levels 1 h post-seizures when compared with the corresponding baseline levels. (F,G) No correlation of P2X7R plasma levels according to sex (F) (Control: p = 0.33; TLE: p = 0.92) or age (G) (Control: r2 = 0.03 p = 0.33; TLE: r2 = 0.003, p = 0.72). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.