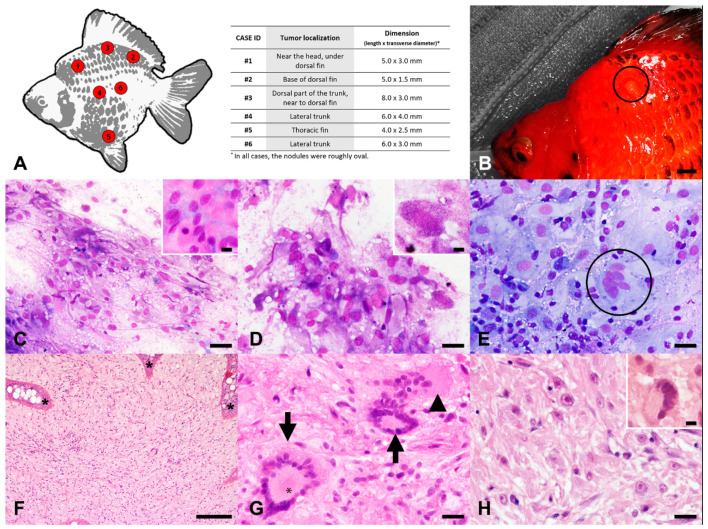
Figure 1.
Atypical neurofibroma, skin, goldfish. (A) Localization of the nodules (left) and corresponding size (table on the right). (B) Case 1: Gross appearance of one of the nodules in situ (encircled). (C) Case 1: Fine needle aspiration smear of the nodule with discrete or loosely cohesive, spindle-shaped to polygonal-shaped atypical cells embedded in a finely fibrillar, compact, and pinkish extracellular matrix (insert). May-Grünwald-Giemsa (MGG). (D) Case 1: Atypical cells with small, magenta intracytoplasmic granules (insert). MGG. (E) Case 6: Presence of occasional multinucleated cells (encircled) within the tumors. MGG. (F) Case 3: Intradermal neoplasm composed of cells arranged in streams, loosely arranged interlacing bundles, whorls, or in a storiform pattern with hyperplasia of the overlying epidermis with rete ridge formation (asterisks). Hematoxylin and eosin (HE). (G) Case 3: Multifocal aggregates of cells palisading around a central area filled with fine eosinophilic fibrils lined by cell cytoplasms (asterisk), resembling rosettes of the pineocytomatous/neurocytic type (arrows), and a giant multinucleated neoplastic cell (arrowhead). HE. (H) Case 2: Spindle-shaped to polygonal-shaped tumor cells displayed moderate to marked anisocytosis, anisokaryosis, and macronucleolosis with prominent magenta nucleoli, with the occasional presence of atypical, large, hyperchromatic nuclei with smudgy chromatin (insert). HE. Scale bars: 0.5 cm (B), 100 µm (F), 20 µm (C–E,G,H), 10 µm ((C) insert, (D) insert, (H), insert).