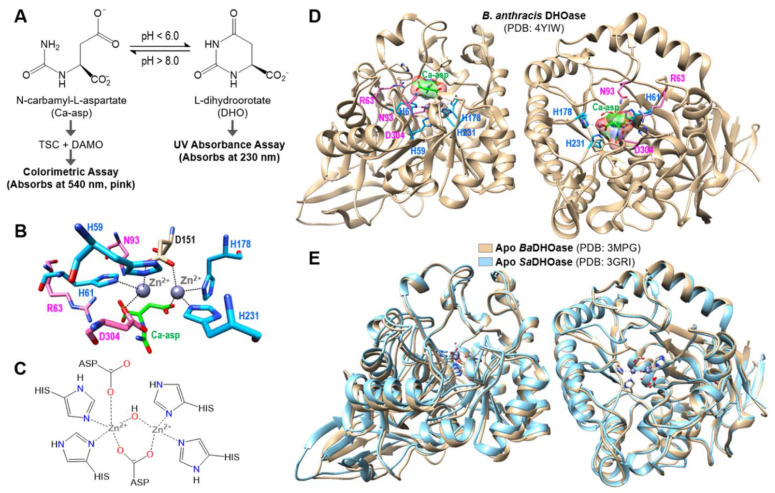
Figure 1.
Background information. (A) The pH-dependent, reversible cyclization of N-carbamyl-L-aspartate (Ca-asp) to L-dihydroorotate (DHO) catalyzed by DHOase. Two assays to detect Ca-asp and DHO. (B) Dimeric structure of Bacillus anthracis DHOase complex with Ca-asp (PDB: 4YIW). The Ca-asp and three catalytic residues (R63, N93 and D304) are shown in green and pink, respectively. Four zinc-binding histidines are in blue. (C) The active site of Class I DHOase displaying two inequivalent Zn (II) ions. (D) The active site of B. anthracis DHOase with Ca-asp bound (PDB: 4YIW). The Ca-asp and three catalytic residues (R63, N93 and D304) are shown in green and pink, respectively. Four zinc-binding histidines are in blue. (E) Overlaid structures of apo DHOases from B. anthracis and S. aureus. Apo BaDHOase and SaDHOase are shown in tan and cyan, respectively.