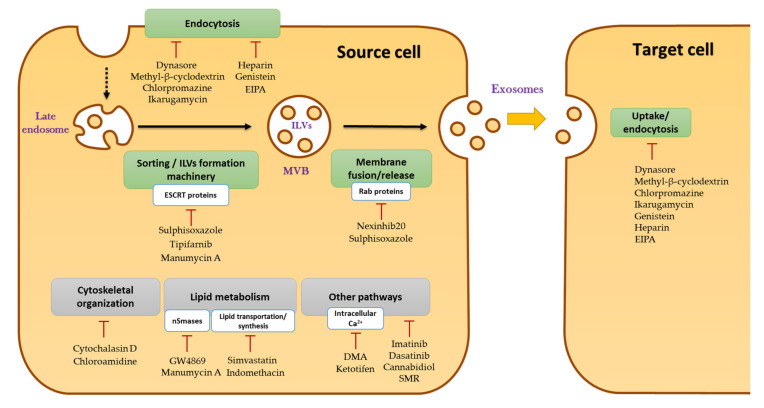
Figure 3.
Cellular processes targeted by drugs inhibiting exosome formation/uptake. Cellular processes involved in exosomal biogenesis or uptake targeted by inhibitors are indicated in green inserts, at times accompanied by the specific components that are being targeted, in smaller inserts. Targeted processes affecting cells generally are indicated in grey inserts. Uptake/Endocytosis: Dynasore, Ikarugamycin, and Chlorpromazine target clathrin dependent endocytosis. Methyl-β-cyclodextrin removes the cholesterol from lipid rafts, and affects essentially caveolin-dependent endocytosis, but also clathrin-dependent endocytosis and macropinocytosis. Heparin inhibits cancer cell surface receptors, which depend on heparin sulfate proteoglycan co-receptors for the uptake of exosomes. Genistein is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor that indirectly interferes with the action of actin and dynamin on the plasma membrane necessary for endocytosis. EIPA can inhibit macropinocytosis. Sorting/ILVs formation: Sulphisoxazole, Tipifarnib, and Manumycin A target signaling pathways leading to depletion of ESCRT-dependent components. Membrane fusion: Nexinhib20 and Sulphisoxazole prevent the fusion of MVBs with the plasma membrane and subsequent exosome release, by inhibiting Rab or other proteins. Cytoskeletal organization is important for the membrane topology rearrangements necessary for vesicle formation, trafficking, secretion, and endocytosis. Cytochalasin D inhibits actin polymerization, which prevents trafficking of MVBs toward the plasma membrane, and may also inhibit macropinocytosis. Chloroamidine prevents the post-translational deamination of actin by the protein PAD (peptidylarginine deiminase), which is required for exosome release and uptake. Lipid metabolism is vital for exosome biogenesis and endocytosis. GW4869 and Manumycin A are selective inhibitors of nSMase2 (neutral sphingomyelinase 2), thereby blocking ceramide-mediated exosome biogenesis. Indomethacin reduces expression of the ABCA3 protein involved in lipid transport. Simvastatin, a cholesterol-lowering drug, decreases levels of the exosomal proteins ALIX, CD63, and CD81. Other pathways: Ketotifen (an antihistamine) and Dimethyl Amiloride (DMA) target intracellular calcium levels, important for regulating exosome release. Imatinib and Dasatinib are inhibitors of tyrosine kinases, while Cannabidiol and SMR are peptides found to inhibit EV release in general (adapted from Hayatudin et al., 2021 [161]).