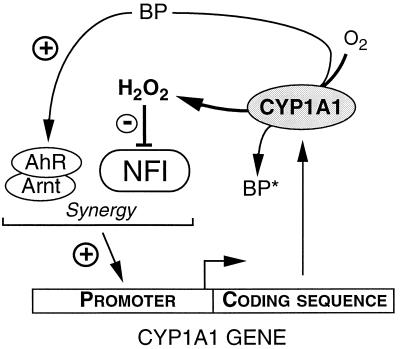
FIG. 9.
Autoregulation of CYP1A1 gene expression. This scheme summarizes the autoregulatory mechanism proposed in this study. The Ah receptor (AhR), after activation by a ligand such as BP, dimerization with Arnt, and interaction with transcription factors, stimulates the CYP1A1 gene promoter. The interaction with NFI leads to a synergistic effect on transcription. This leads to the synthesis of the enzyme. CYP1A1 enzymatic activity generates H2O2, especially in the presence of uncoupled substrates such as BP (which can be converted into a metabolite [BP*]). H2O2 then alters NFI function, mainly at the level of its TAD. In consequence, NFI loses its ability to activate the CYP1A1 gene basal promoter activity and to act in synergy with the AhR signaling, which limits the expression of the CYP1A1 enzyme.