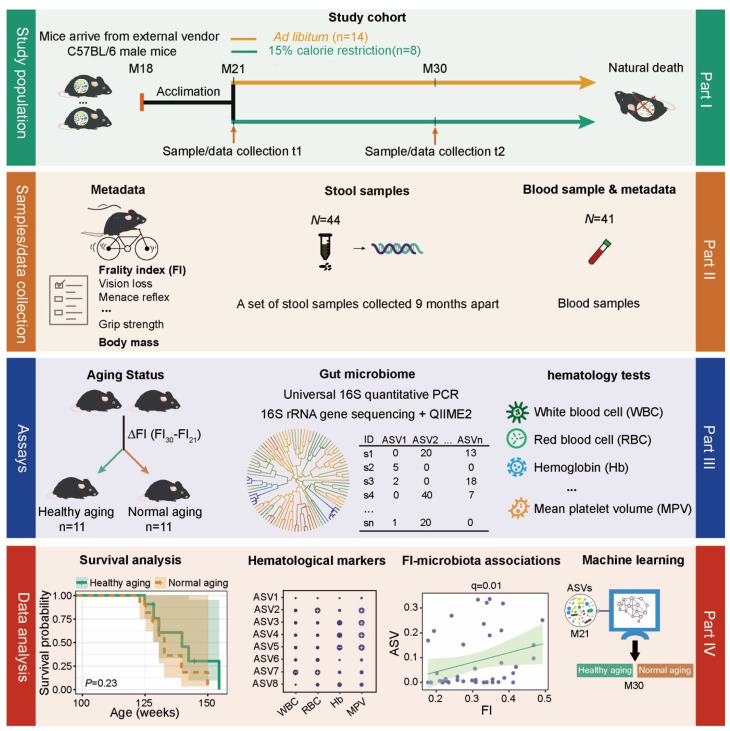
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram showing the experimental design. The study cohort was comprised of 22 adult male C57BL/6 mice, which were recruited into the study at 21 months of age after having been maintained since birth under standard husbandry conditions (see Methods). We collected blood and fecal samples and measured frailty using a compound index at 21 months (baseline) and 30 months of age. Following baseline measurements, we randomly divided these mice into two diet groups, fed either ad libitum (AL, n = 14) with standard chow or under mild (15%) calorie restriction (CR, n = 8). Mice were then followed longitudinally until death. We performed universal 16S quantitative PCR (qPCR) to quantify absolute bacterial abundance and 16S rRNA gene sequencing to determine taxonomic composition, using QIIME2 to characterize the ASV microbial features. Blood markers were measured using standard methods. We then used the median FI change (denoted as ΔFI) between 21 and 30 months of age to delineate healthy versus normal aging.