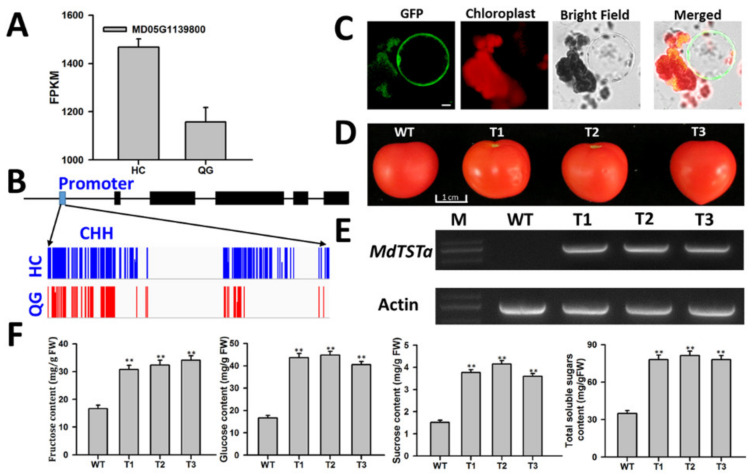
Figure 5.
Functional characterization of MdTSTa. (A) MdTSTa expression levels in ‘HC’ and ‘QG’ mature fruits. (B) Differences in the methylation level of the MdTSTa promoter in the CHH context between ‘HC’ and ‘QG’ mature fruits. (C) Tonoplast localization of the MdTSTa-GFP fusion protein in vacuoles, which were obtained after transiently transformed N. benthamiana protoplasts were lysed. Bars represent 10 μm. (D) Mature tomato fruits from wild-type and 35S: MdTSTa transgenic lines. (E) MdTSTa expression in wild-type and transgenic tomato based on RT-PCR data. (F) Soluble sugar contents in the mature tomato fruits of wild-type and transgenic lines. WT: wild-type; T1, T2, and T3: 35S: MdTSTa transgenic lines. Double asterisks (**) represent significant differences between wild-type and transgenic fruits (t-test, p < 0.01).