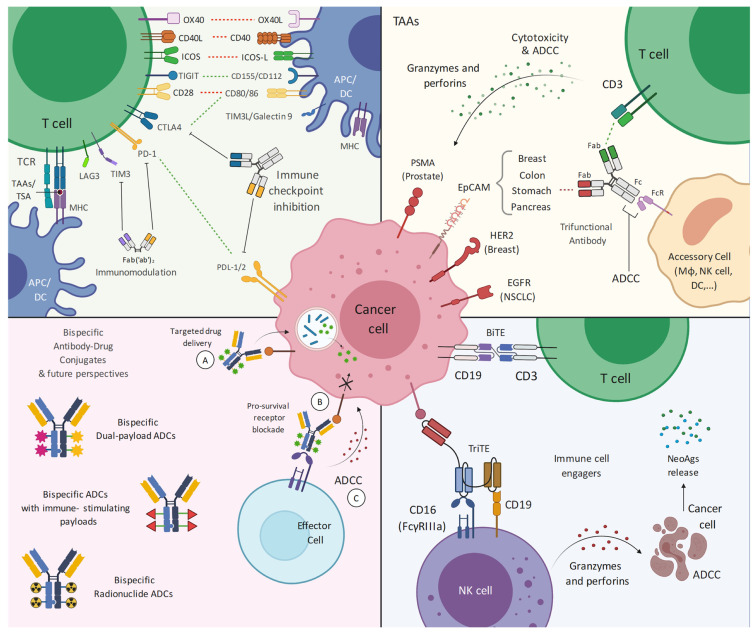
Figure 1.
Main design, applications, and future perspectives of bispecific antibodies and engagers. Each quadrant represents different applications of bi- and tri-specific novel technologies. Upper left panel: dual immune checkpoint blockade by means of bispecific antibodies or nanobodies. Co-targeting of multiple co-stimulatory molecules has been exploited either to enhance immune checkpoint inhibition or to combine immune checkpoint blockade and immunomodulation. Red-dashed lines: co-stimulatory molecules; green-dashed lines: co-inhibitory molecules. Upper right panel: bispecific antibodies targeting dual tumor-associated antigens. Trifunctional properties of bsAbs comprise an appropriate Fc region in order to not only recruit T-cells, but also accessory cells bearing activating FcγR. Hence, additional T-cell-activating signals and presentation of tumor-derived antigens to T-cells can be provided; Lower left panel: bispecific antibody-drug conjugates are investigational strategies aiming at exploiting both the target-specific properties of engineered antibodies and the cytotoxic activity of payloads; Lower right panel: most immune cell engagers are trans-binding bispecific antibodies (bsAbs) usually consisting of two linked single-chain fragment variables (scFvs) that originate from different monoclonal antibodies: one scFv recognizes a surface TAA, whereas the other is specific for a certain membrane molecule expressed on effector immune cells. Abbreviations: OX40, Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 4 or TNFRSF4; OX40L, OX40 ligand; ICOS, Inducible costimulator; ICOS-L, Inducible costimulator-ligand (ICOS-L); CD, cluster of differentiation; TIGIT, T cell immunoreceptor with Ig and ITIM domains; TIM3, T-cell immunoglobulin mucin 3; TIM3L, T-cell immunoglobulin mucin 3 ligand; CTLA-4, Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte Antigen 4; PD-L1, Programmed death-ligand 1; PD-1, Programmed Death 1; TCR, T-cell receptor; LAG3, Lymphocyte-activation gene 3; MHC, Major Histocompatibility Complex; TAA, tumor-associated antigen; TSA, tumor-specific antigen; Fab, antigen-binding fragment; Fc, fragment crystallizable region; FcR, fragment crystallizable region receptor; APC, antigen-presenting cell; DC, dendritic cell; ADC, antibody-drug conjugates; ADCC, antibody-dependent cytotoxicity; PSMA, prostate-specific membrane antigen; BiTE, Bi-specific T-cell engager; TriTE, trispecific T-cell engager; EpCAM, Epithelial cell adhesion molecule; HER2, Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2; NK, natural killer cell; NeoAgs; neoantigens; FcγRIIIA, Fc Gamma Receptor IIIa; Mφ, macrophage; NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer. Created with BioRender.com.