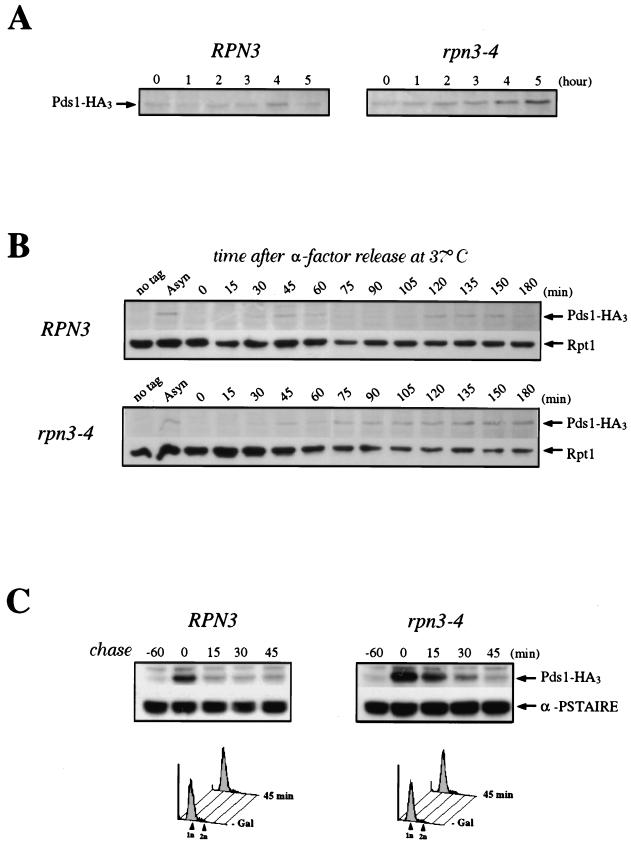
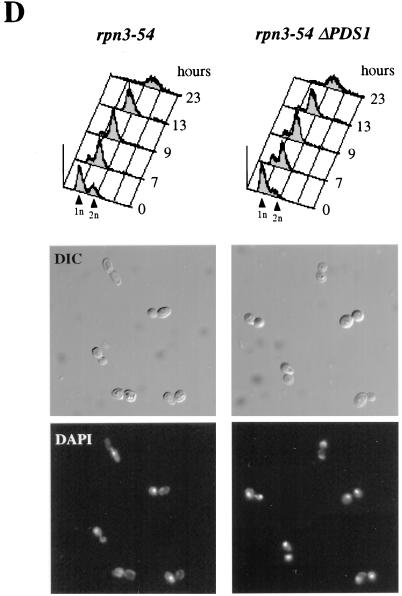
FIG. 5.
Role of Rpn3 in the proteolysis of Pds1. (A) Early-log-phase cultures of wild-type YE103 (RPN3) cells and YE104 mutant (rpn3-4) cells carrying an HA-tagged PDS1 gene were shifted from 25 to 37°C as described in the legend to Fig. 3A and analyzed by immunoblotting with an anti-HA antibody (Pds1-HA3) to monitor Pds1 levels at the indicated times. (B) Cell cycle regulation of Pds1 in the rpn3 mutant. Early-log-phase cultures of wild-type YE103 (RPN3) cells and YE104 mutant (rpn3-4) cells carrying an HA-tagged PDS1 gene were arrested in G1 with α-factor and then released into fresh medium lacking α-factor at 37°C. Samples for immunoblot analysis of HA-tagged Pds1 were withdrawn at the indicated times. Extracts from the wild-type strain with untagged PDS1 (no tag) were used as a control. A sample was also taken before the addition of α-factor as a source of asynchronous cells (Asyn). The 19S regulatory subunit Rpt1/Cim5 was immunodetected with specific antibodies as a loading control. (C) Reduced Pds1 turnover in the rpn3 mutant. Control YE108 (RPN3) cells and rpn3 mutant YE109 (rpn3-4) cells, both carrying an HA-tagged PDS1 gene under the control of the inducible GAL1 promoter, were grown in YEPR medium, arrested in G1, shifted to 37°C, and induced to express Pds1 for 60 min. Samples were collected before (lane −60) and after (lane 0) Pds1 induction and every 15 min after transfer of the cells to prewarmed α-factor-containing YEPD medium. A Cdc28 immunoblot is shown as a loading control (α-PSTAIRE). FACScan analysis of the first and last samples from this experiment is shown for each strain. (D) PDS1 deletion bypasses the metaphase arrest terminal phenotype of Rpn3-depleted cells. rpn3-54 (YE231) and rpn3-54 ΔPDS1 (YE416) cells, whose sole source of Rpn3 is expression from the GAL1 promoter, were inoculated into galactose-containing medium at 25°C. Rpn3 depletion was then induced at time zero by transferring both cultures to glucose-containing medium. At the indicated times, samples were collected for determination of their cellular DNA contents by flow cytometry. Cell samples were also recovered from the last (23-h) time point for phenotypic analysis of the arrested cells. DIC, differential interference contrast; DAPI, nuclear staining as observed with the DNA dye DAPI.