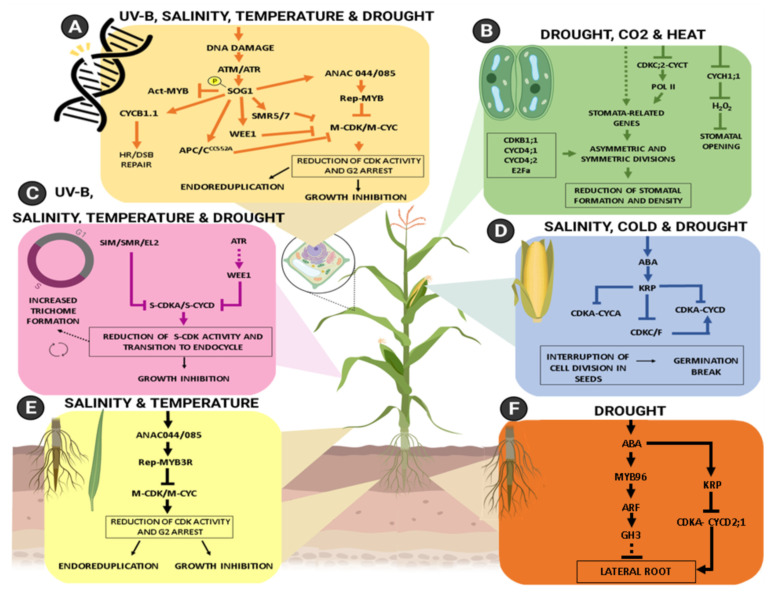
Figure 2.
Cyclin-dependent kinases acting as part of intracellular signaling cascades that respond to a number of environmental stresses. Due to climatic events, adaptability strategies are triggered by plants to overcome stressful conditions. Excess CO2 in the atmosphere causes temperature fluctuations, intensifying water scarcity, which can aggravate the levels of salt concentration in the soil. To face these limitations imposed by the environment, plants undergo molecular, physiological, and mainly morphological changes. CDKs, together with cyclins, play an important role in primary responses to cellular processes that aid in plant survival. According to the modulation of the environment, strategies such as the interruption of germination (D), G1-S arrest by the action of CDK inhibitors SIM/ SMR/EL2 and WEE1 (C), and G2 arrest triggered by a decrease in CDK activity as part of a SOG1-dependent DNA damage response that also involves different CKIs (A) lead to growth inhibition and often transition to endoreduplication. The reduction in stomatal density, minimizing water loss (B) and SOG1-independent cell cycle arrest at G2 leading to growth inhibition in situations of excessive salinity and temperature (E) are also considered plasticity strategies. Eventually, it becomes necessary to drive the metabolism towards the formation of new organs, such as the increase of main roots during drought (F) and the formation of trichomes stimulated under different stresses to minimize evaporation and regulate temperature (C). Abbreviations: ACT-MYB—activator-type MYB3R; REP-MYB—repressor-type MYB3R; HR—homologous recombination; DSB—double strand break; SOG1—suppressor of gamma response 1; ATM—ataxia telangiectasia mutated; ATR—ATM and RAD3-related; DDR—DNA damage response; CDK—cyclin-dependent kinase; CYC—cyclin; APC/C—anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome; SIM—siamese; CKI—CDK inhibitor; NAC—domain transcription factors; SMR—siamese-related; POL II—RNA polymerase II; ABA—abscisic acid; KRP—KIP-related protein; ARF—auxin response factor; GH3—gretchen hagen 3. Dotted arrow—indirect mechanism; continuous arrow—induction; block arrow—repression. Created with BioRender.com.