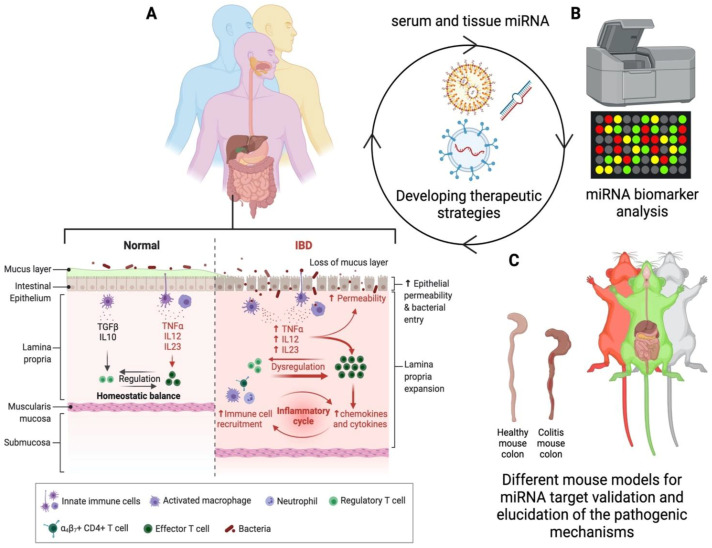
Figure 1.
miRNA therapeutics: human–mouse–human translational cycle. (A) miRNAs derived from tissue biopsies and serum depict IBD hallmarks, including a dysregulated immune system and disrupted intestinal barrier function. (B) miRNAs can be profiled to determine differential levels between IBD patients and healthy volunteers. (C) Differentially expressed miRNAs and the complex mechanisms through which miRNAs regulate gene expression can be studied and validated in appropriate murine colitis models, including humanized mouse models and highly genetically diverse mouse strains, which are excellent resources for recapitulating human genetic diversity to elucidate the therapeutic potential of miRNAs. Based on preclinical animal data, therapeutic strategies can be developed, utilizing natural or synthetic nanoparticles.