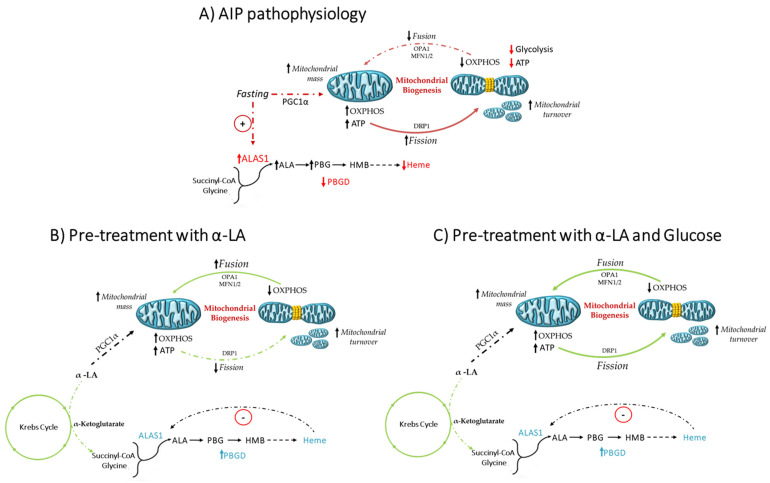
Figure 4.
Schematic representation of metabolic alterations and the efficacy of α-LA in siPBGD cells during fasting. (A) Fasting induced mitochondrial biogenesis through PGC1α, possibly worsening mitochondrial injury by shunting mitochondrial dynamics toward fission, which was mediated by DRP1, and inhibiting OPA1 and MFN2, which provide the fusion of mitochondrial inner and outer membranes. The accumulation of divided mitochondria lowered OXPHOS ability and exacerbated ATP shortfall. (B) Pre-treatment with α-LA in siPBGD cells even promoted PGC1α activity, but it improved OPA1 and MFN2 expression, thereby enhancing mitochondrial fusion, which is a condition that could support OXPHOS activity during energy demand. (C) Pre-treatment with α-LA and glucose may recover the overall mitochondrial wellness by acting at multiple levels. On one hand, α-LA may improve heme biosynthesis, which is a mechanism occurring in the mitochondrial matrix. On the other hand, α-LA may enhance glycolysis, ATP production, and OXPHOS, possibly sustaining the Krebs cycle. The restoration of hepatocellular homeostasis could allow recovering mitochondrial dynamics, in terms of fusion, fission, and overall mitochondrial mass.